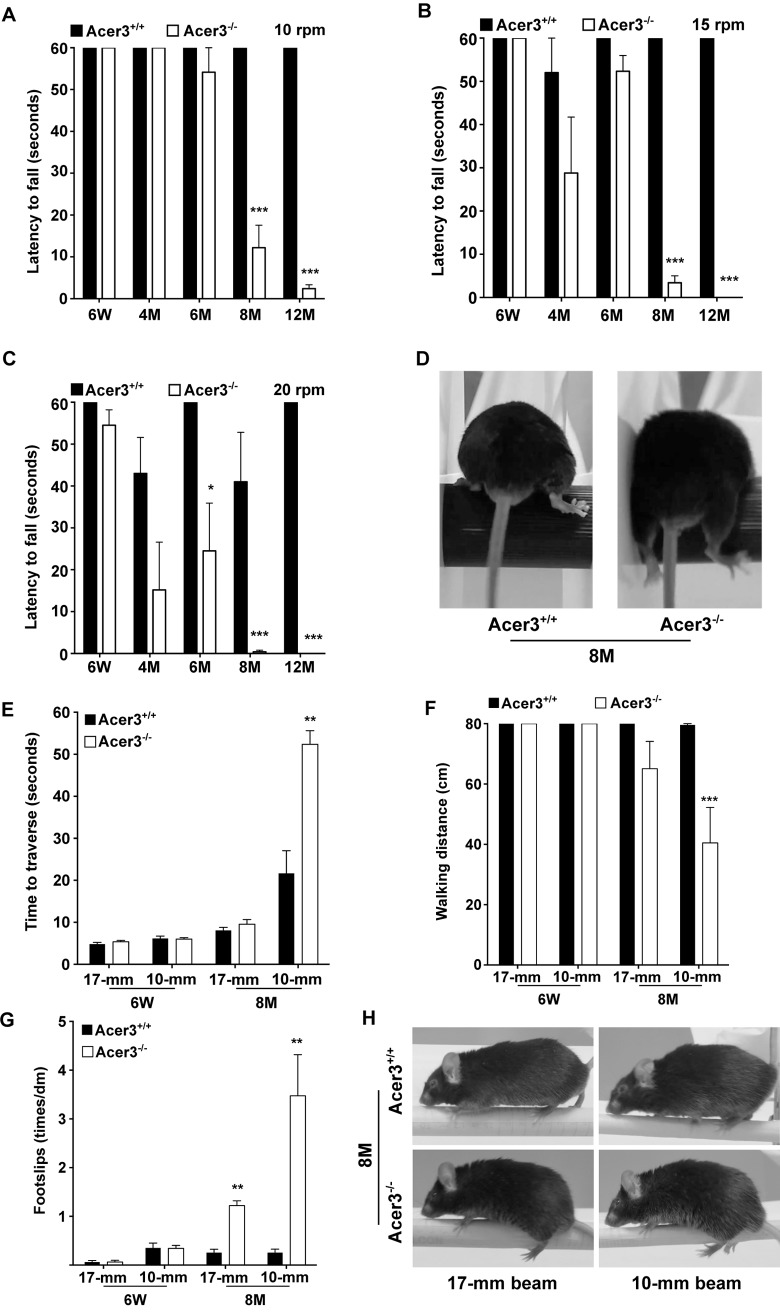
Fig 7. Acer3 knockout impairs motor coordination and balance capabilities in mice.
A-D. Rotarod tests for motor coordination. Acer3+/+ and Acer3-/- mice at 6W, 4M, 6M, 8M, or 12M of age were subjected to rotarod tests under 3 task difficulties—10, 15, and 20 rpm, respectively. Hindlimb step patterns in a representative Acer3+/+ and Acer3-/- mouse at 8M of age at 20 rpm are displayed in D. Note that the hindpaws of Acer3-/- mice, but not those of Acer3+/+ mice slipped off the rod. E-H. Beam walking tests for motor coordination and balance capabilities. Acer3+/+ and Acer3-/- mice at 6W or 8M of age were subjected to beam walking tests under two task difficulties. The average of three trials were quantitatively analyzed for time to traverse the beam (E), walking distance (F), and foot-slips of hindpaws (G). Patterns of hindpaw contacting the beam during walking in a representative 8-month-old Acer3+/+ and Acer3-/- mouse are displayed in H. Note the foot-slips for both beam walking conditions in the Acer3-/- mouse. The data in A, B, C, E, F, and G represent mean values ± SD, n = 5–8. n.s., not significant.