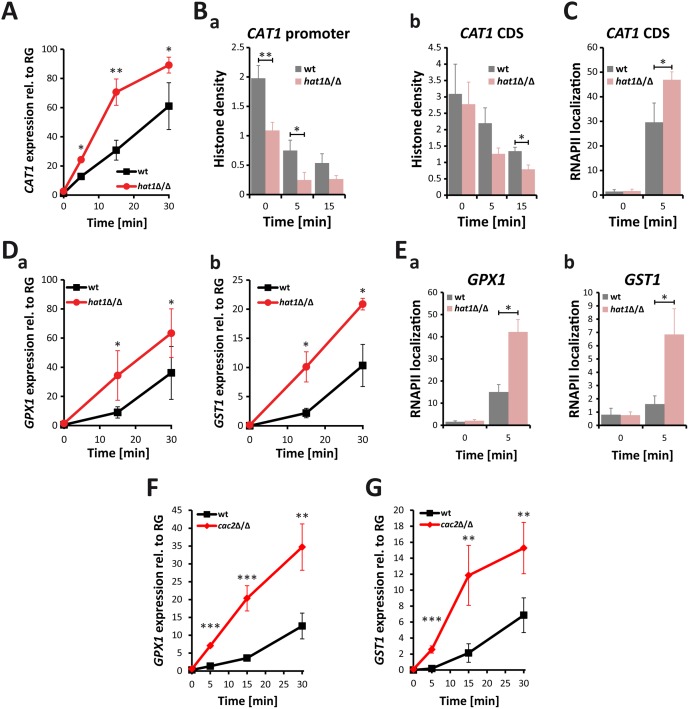
Fig 6. Lack of Hat1 accelerates induction of oxidative stress genes.
(A) Catalase induction rate is strongly increased in hat1Δ/Δ cells. CAT1 expression levels were measured by RT-qPCR after induction with 1.6 mM H2O2 at the indicated time points. Transcript levels were normalized to the expression level of the reference gene (RG) PAT1. Data are shown as mean + SD from 3 independent experiments. (B) Histone density at the CAT1 locus is reduced in cells lacking Hat1. Histone H3 occupancy was determined by ChIP at the CAT1 promoter region (a) and the CDS (b). (C) Loss of Hat1 leads to increased RNAPII recruitment at the CAT1 locus. RNAPII levels were determined by ChIP at the CAT1 CDS. (D) Induction rate of glutathione-utilizing enzymes is increased in hat1Δ/Δ cells. GPX1 (a) and GST1 (b) expression levels were determined by RT-qPCR at the indicated time points. Experiment was performed as described in (A). (E) Lack of Hat1 leads to increased RNAPII recruitment at the GPX1 and GST1 loci. RNAPII levels were determined by ChIP at the GPX1 (a) and GST1 (b) genes. (F+G) Loss of Cac2 increases the induction rate of both GPX1 and GST1 following H2O2 treatment. Experimental conditions were used as described in (A).