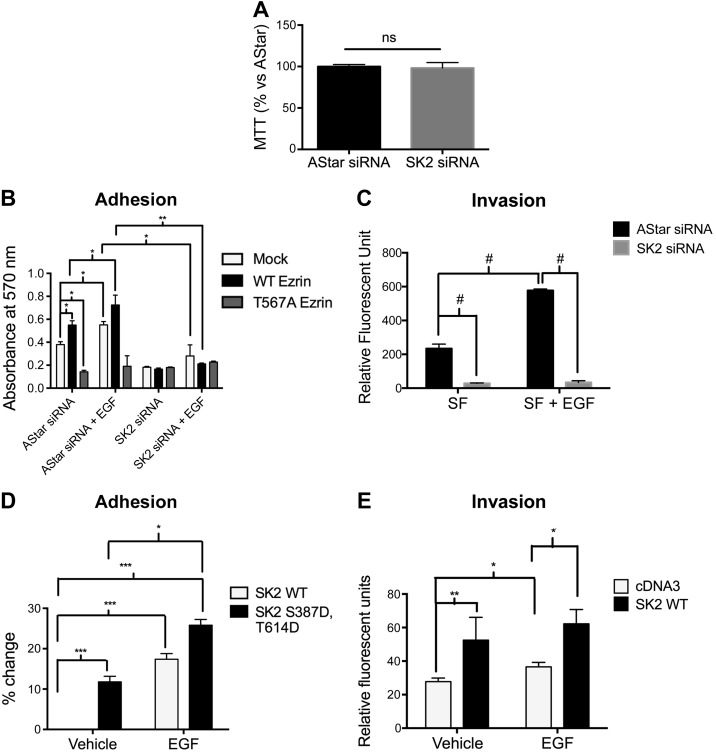
Figure 4.
SK2 is required and sufficient for cell adhesion and invasion toward EGF. A) HeLa cells were treated with AStar or SK2 siRNA for 48 h. Cells were then starved for 4 h. An MTT assay was then performed as described in the Materials and Methods. B) HeLa cells were treated with AStar or SK2 siRNA for 24 h. Cells were then transfected with mock, WT ezrin, or Thr567A ezrin DNA for another 24 h. Cells were then starved for 4 h, trypsinized, and plated on fibronectin-coated plates. Cells were then treated with vehicle (PBS) or EGF (10 ng/ml) for 12 h. MTT assay was then performed, and absorbance was measured as a quantification of cell number. C) HeLa cells were treated with AStar or SK2 siRNA for 48 h. Cells were then starved for 4 h prior to their plating in the apical chamber of Matrigel-coated transwell inserts and allowed to invade for 36 h toward serum-free or EGF-supplemented medium. Invading cells were then stained with 4 μg/μl calcein AM, and absorbance was read in a plate reader as described in the Materials and Methods. D) HeLa cells were transfected with WT SK2 or Ser387D;Tyr614D SK2 DNA for 24 h. Cell adhesion was then assessed as described in (B). E) HeLa cells overexpressing cDNA3 or WT SK2 were plated in the apical chamber of Matrigel-coated transwell inserts and allowed to invade for 36 h toward serum-free or EGF-supplemented medium. Invaded cells were then quantified as previously described. The data represent means ± se of 3 independent experiments. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; #P < 0.0001.