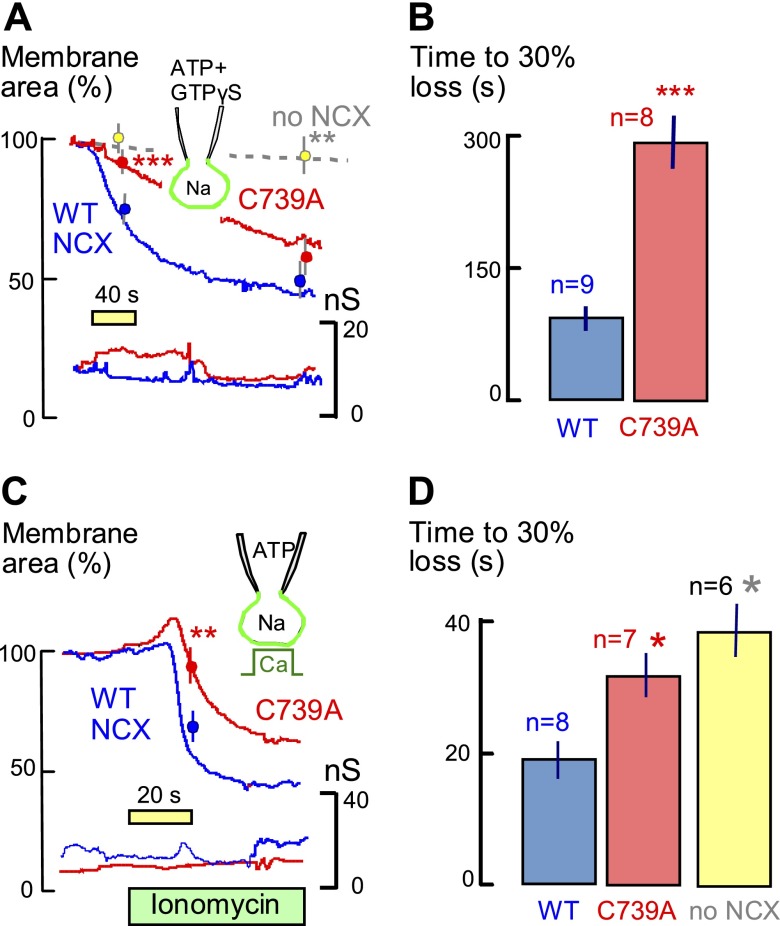
Figure 7.
Impact of palmitoylation of NCX1 on massive endocytosis occurring in response to excessive G-protein activation and Ca influx. Stably transfected FT-293 cells expressing WT and C739A NCX1 were voltage clamped in the whole-cell mode with 8 mM MgATP in the pipette solution. A) Using a highly Ca-buffered cytoplasmic solution (10 mM EGTA with 1 mM Ca) with 0.25 mM GTPγS, cells expressing WT exchangers internalize 33 ± 3% of their membrane within 40 s of establishing the whole cell configuration, whereas cells expressing C739A exchangers internalize only 10 ± 2%. (P < 0.001). At 3 min, the difference between exchanger-expression cells is not significant, and membrane loss in cells without exchangers is negligible. B) Quantitation of endocytosis as the time required to decrease membrane area by 30%. C739A-expressing cells internalize at a rate that is >3 times less than cells expressing WT exchangers. C) Using a weakly Ca-buffered cytoplasmic solution (0.5 mM EGTA with 0.25 mM Ca), extracellular Ca (2 mM) is applied with 7 μM ionomycin to promote Ca influx. In WT-expressing cells, small initial exocytic responses (i.e., with increasing membrane area) are followed by loss of 50% of the cell surface within about 20 s. In C739 cells, the exocytic responses are larger and endocytic responses are delayed. The loss of membrane area in cells expressing WT exchangers amounts to 33 ± 4%, and loss of membrane in C739A-expressing cells amounts to only 13 ± 6% (P < 0.01). D) Quantitation of Ca-induced endocytic responses as the time required to remove 30% of the cell surface. Endocytosis times are increased by >50% in C739A cells, compared with WT cells (P < 0.05), and endocytosis times are doubled in cells that do not express NCX1 (P < 0.01). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.