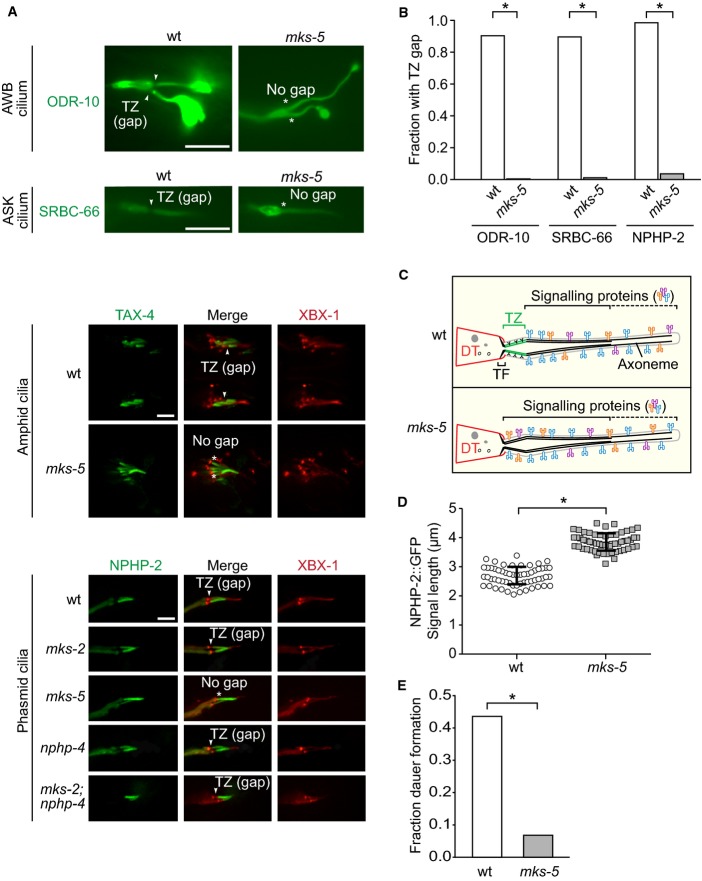
A ciliary zone of exclusion (CIZE) established by MKS-5 compartmentalises signalling molecules to the more distal regions of the axoneme and is required for efficient signal transduction (dauer formation)
EGFP-tagged SRBC-66 and ODR-10 both localise to the entire axonemes of ASK and AWB neuron cilia, respectively, and are excluded from the TZ in wild type (wt); these markers occupy the entire cilium, including the TZ, in mks-5 mutants. TAX-4 and NPHP-2, orthologues of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel CNGA1 and NPHP2/inversin respectively, which are found in the inversin (Inv) compartment in wt, also localise to the TZ in mks-5 animals. NPHP-2::EGFP was co-localised with XBX-1::tdTomato and are shown in the phasmid cilia while TAX-4::EGFP is shown in amphid cilia. den, dendrite; TZ, transition zone; BB, basal body; arrowheads indicate gap is present; * indicates no gap. Scale bars: 4 μm.
Quantification of cilia observed to have a clear gap in signal (i.e. CIZE) at the TZ in wt animals compared to mks-5 mutants for the ODR-10, SRBC-66, and NPHP-2 protein markers. *P < 0.001, chi-squared test.
Schematic depicting the CIZE, which excludes signalling proteins from the TZ in wt animals but not mks-5 animals, which lack TZ ultrastructure.
NPHP-2 signal length is longer in mks-5 animals compared to wt, consistent with the presence of an axonemal region that lacks TZ ultrastructure. *P < 0.001, t-test, error bars are standard deviation.
The mks-5 mutant displays a dauer formation phenotype compared to wild-type when presented with synthetic ASCR#2 dauer pheromone. ASCR#2 is detected by the SRBC-66 G-protein-coupled receptor, and downstream signalling includes the cGMP-dependent channel, TAX-4. *P < 0.001, chi-square test.