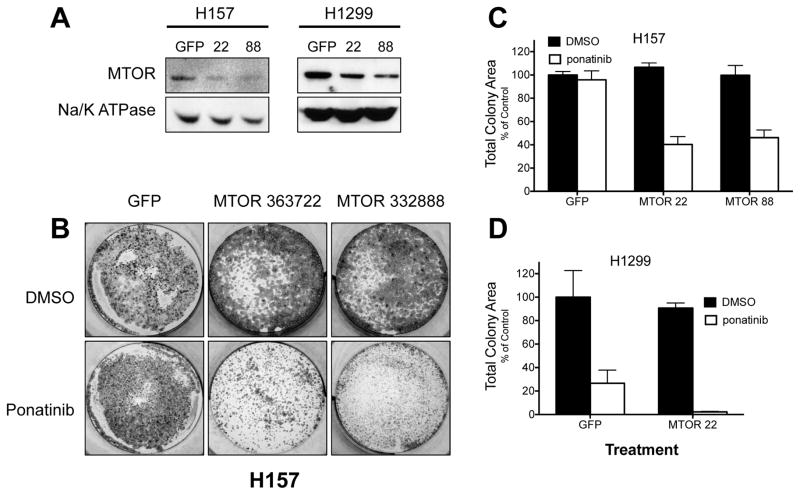
Figure 1. Validation of MTOR as a synthetic lethal gene with FGFR inhibition by RNAi-mediated knockdown.
A, H157 and H1299 cells were transduced with either a negative control shRNA targeting GFP, or one of two independent MTOR targeting shRNAs (TRCN0000363722 or TRCN0000332888), henceforth abbreviated as MTOR 22 and MTOR 88, respectively. Cells were selected for resistance to puromycin and resulting colonies were harvested and immunoblotted for MTOR protein levels. The protein level of the α-subunit of Na/K-ATPase was measured as a loading control. B, As in A except H157 cells were treated with 300 nM ponatinib or DMSO at the time of puromycin selection. Resulting colonies were stained with crystal violet and photographed. A representative well of three replicates is shown. Mean total colony area (± SEM, n=3) for the indicated shRNA transductions and ponatinib treatments were quantified as described in the Materials and Methods and the data are graphically presented for H157 (C) and H1299 cells (D), respectively.