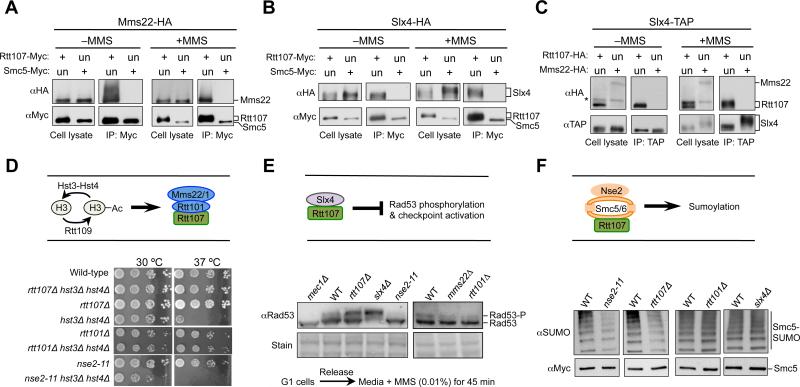
Figure 1. Rtt107 forms separate complexes with its three partners.
(A-C) The three Rtt107 binding partners do not associate among themselves. Cells were grown in the presence or absence of 0.03% MMS (2 h). Immunoprecipitation of Myc-tagged Rtt107, but not Smc5, co-purifies Mms22 (A) or Slx4 (B). Immunoprecipitation of TAP-tagged Slx4 co-purifies with Rtt107, but not Mms22 (C). An upward shift of Rtt107 and Slx4 bands in MMS-treated samples is due to phosphorylation (Flott and Rouse, 2005; Roberts et al., 2006; Rouse, 2004). The asterisk denotes a background band. Un: untagged; +: tagged versions of proteins. Note that longer exposures of western blots confirm that Smc5 and Mms22, which are less abundant than Rtt107, do not associate with Slx4 nor between themselves.
(D) Mutants of Rtt101 or Rtt107, but not Nse2, rescue the temperature sensitivity of hst3Δ hst4Δ cells. Ten-fold serial dilutions of cells were spotted. H3: newly synthesized histone H3.
(E) Mutations of Slx4 or Rtt107, but not Rtt101Mms22 and Nse2, increase the levels of Rad53 phosphorylation. -P: phosphorylated form. Equal loading is shown by stain.
(F) nse2-11 or rtt107Δ, but not slx4Δ or rtt101Δ, reduces the sumoylation levels of Smc5. Cells were treated with 0.03% MMS for 2 h, and Smc5-Myc was immunoprecipitated and analyzed by Western blot using a SUMO-specific antibody (top) that recognizes the sumoylated forms, and a Myc antibody that detects the unmodified forms (bottom).
See also Figure S1.