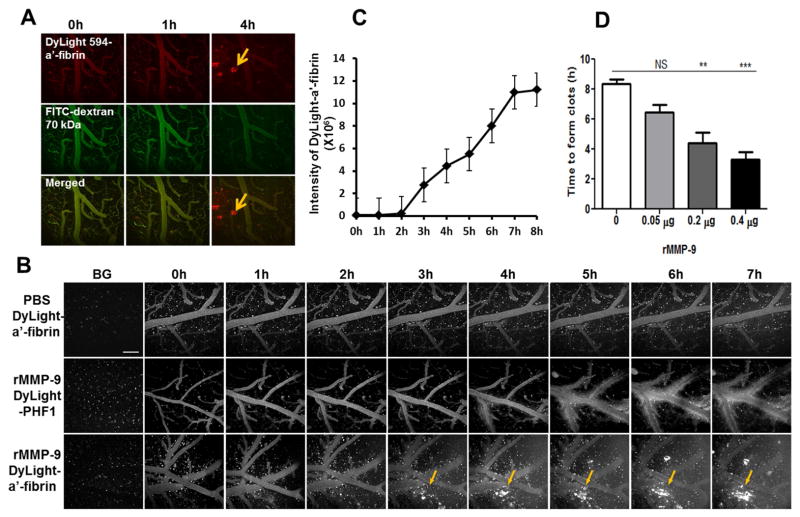
Fig. 3. Real-time visualization and quantitation of lobar hemorrhage in vivo by multi-photon microscopy.
C57/BL6 mice, 3 months of age, were prepared with a craniotomy followed by removal of the dura mater. PBS or rMMP-9 (0.4 μg) was topically applied to the surface of mouse brains. Fluorescence-conjugated macromolecules were used as tracers. Animals were imaged hourly using a Fluoview 1000MPE Olympus multi-photon microscope to track the vascular leakage. The background images (BG) were acquired by imaging animals before administration of rMMP-9 and a tracer. (A) Examination of MMP-9-induced hemorrhage using fluorescent-anti-fibrin tracer. A mixture of a DyLight 594-conjugated anti-fibrin antibody (DyLight 594-α′-fibrin) and a fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated dextran (FITC-dextran, 70 kDa) was intravenously infused into tail veins of animals. Pre-activated rMMP-9 (0.4 μg) was topically applied to the surface of mouse brains followed by simultaneously imaging hourly in two channels to track the fluorescence signals of both DyLight 594-anti-fibrin (upper panel) and FITC-dextran (middle panel). The fluorescence signals of the DyLight 594-anti-fibrin or the FITC-dextran were merged to compare the detection sensitivity of the two tracers (lower panel). Arrows: fluorescent clots recognized by the fluorescent-anti-fibrin tracer. Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) The specificity of the fluorescent-anti-fibrin tracer in detecting of rMMP-9-induced lobar hemorrhage. Mice treated with 0.4 μg of rMMP-9 (middle and lower panels) or PBS (upper panel) were processed for hemorrhage assessment. DyLight 594-anti-fibrin (DyLight-a′-fibrin, upper and middle panels) or DyLight 594-conjuaged PHF1 antibody (DyLight-PHF1, lower panel) was used as a tracer. Arrows showing the fluorescent clots recognized by DyLight 594-a′-fibrin. Scale bar = 100 μm. (C) The volume of hemorrhage was determined by quantifying the fluorescence intensity of DyLight 594-anti-fibrin that accumulated at the clots. (D) Effects of different doses of rMMP-9 on hemorrhage induction. PBS (0 μg of rMMP-9) or rMMP-9 at dose of 0.05 μg, 0.2 μg, or 0.4 μg were topically applied to the mouse brains. Mice were processed for imaging hourly up to 7 hours of time period. DyLight 594-anti-fibrin was used as a tracer. The time that the clots were first detected (time to form clots) was measured. NS = not significant; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 vs PBS treatment (0 μg). n = 3 – 5.