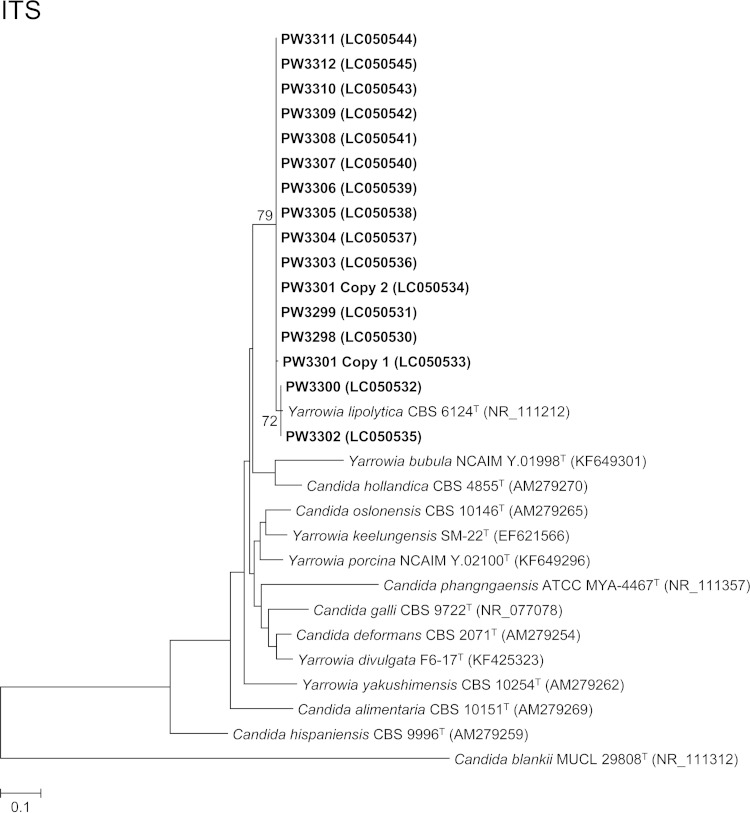
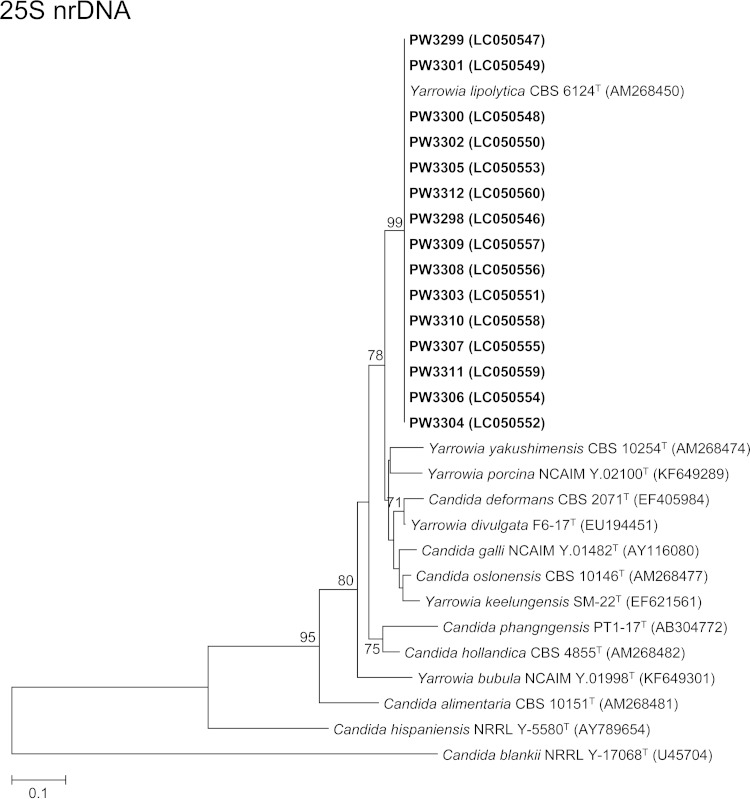
FIG 2.
Phylogenetic trees showing the relationship between the 15 fungal isolates and other members of the Yarrowia clade. The trees were inferred from ITS and 25S nrDNA sequence data by the maximum likelihood method with the substitution models T92 (Tamura 3-parameter model) + G (gamma-distributed rate variation) and K2 (Kimura 2-parameter model) + G, respectively. The numbers of nucleotide positions of the trimmed, aligned sequences included for phylogenetic analyses are 293 and 488, respectively. The trees were rooted using Candida blankii strains MUCL 29808T and NRRL Y-17068T, respectively. The scale bars indicate the estimated numbers of substitutions per base. The numbers at the nodes, expressed in percentages, indicate levels of bootstrap support calculated from 1,000 trees, and bootstrap values lower than 70 are not shown. All accession numbers (in parentheses) are given as cited in the DDBJ/ENA/GenBank databases. The case isolates reported in this study are highlighted in bold type.