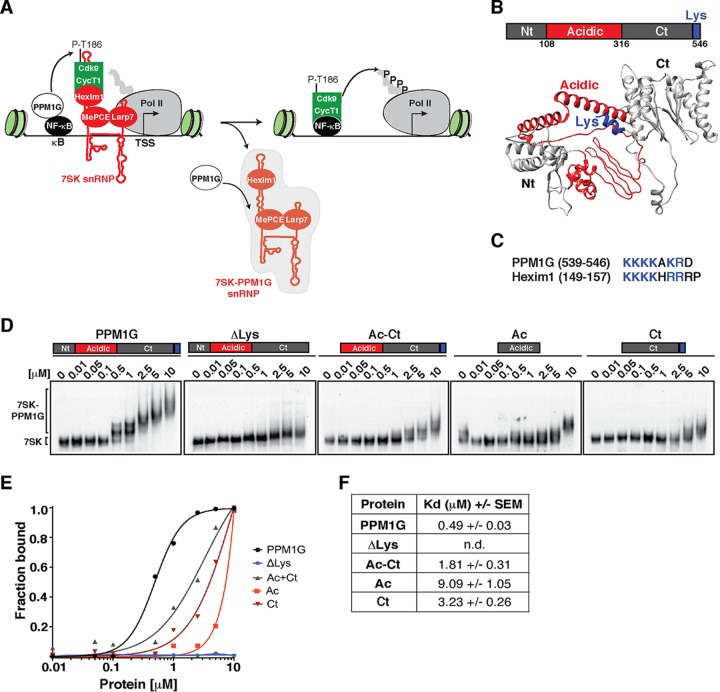
FIG 1.
The PPM1G phosphatase binds 7SK RNA using its C-terminal Lys-rich domain. (A) Proposed model for the role of PPM1G in the NF-κB transcriptional program. PPM1G is recruited by NF-κB to target genes in response to environmental stimuli, where it dephosphorylates the T-loop of Cdk9 (P-T186), thereby promoting its uncoupling from Hexim1 and its release from the inhibitory, promoter-bound 7SK snRNP complex. In this process, PPM1G subsequently binds 7SK RNA, possibly forming a 7SK-PPM1G snRNP complex lacking P-TEFb. (B) Domain organization of human PPM1G and representation of each domain in the predicted three-dimensional structure. Nt, N-terminal domain; Ac, acidic region; Ct, C-terminal domain; Lys, Lys-rich region. (C) Alignment of PPM1G and Hexim1 Lys-rich regions with their positions indicated in parentheses. (D) Gel shift assays with 7SK RNA and increasing amounts of full-length PPM1G or domains. (E) Binding curves from the gel shifts shown in panel D. (F) Calculations of the apparent dissociation constants (Kdapp) from data in panel E. Kdapp values represent the averages of data from three independent experiments with the standard errors of the means (n = 3). n.d., not determined, because the data set does not enable accurate calculation of the Kdapp values.