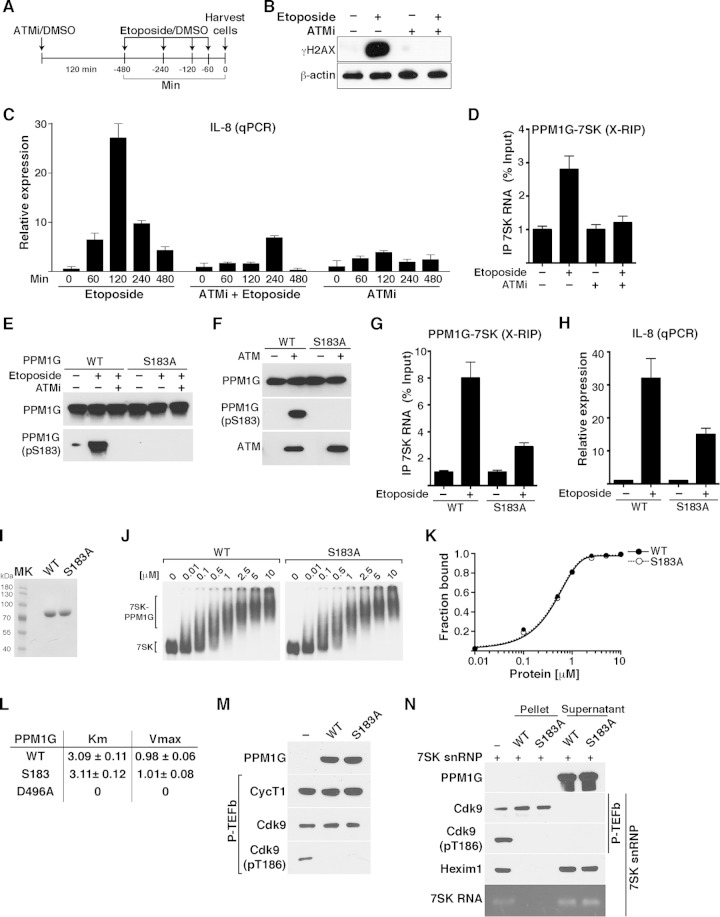
FIG 8.
PPM1G-7SK RNA interaction and activation of NF-κB transcription in response to DNA damage are ATM kinase dependent. (A) Scheme showing the protocol used to pretreat HeLa cells with ATMi (or DMSO as a control) for 120 min, followed by a time course of etoposide treatment or DMSO. (B) Validation of ATM inhibition with an ATMi by Western blotting with γH2AX antibody. HeLa cells were pretreated for 120 min with an ATMi or DMSO as a control, followed by a 120-min etoposide or DMSO treatment. Cell pellets were used for Western blotting with the indicated antibodies (β-actin was used as a loading control). (C) ATM inhibition blocks NF-κB transcription (IL-8 gene) from HeLa cells in response to etoposide. Cells were pretreated with an ATMi or vehicle (DMSO) for 120 min and sequentially treated with etoposide or vehicle (DMSO) for the time points indicated. Total RNA was then extracted, and the IL-8 gene expression level, normalized to the β-actin level, was calculated by qRT-PCR (means ± standard errors of the means; n = 3). (D) ATM inhibition abolishes the PPM1G-7SK protein-RNA interaction in response to etoposide. HeLa cells were pretreated (+) or not pretreated (−) with an ATMi (120 min), followed by a 30-min treatment with etoposide or DMSO (−). Cells were cross-linked with formaldehyde, and endogenous PPM1G was immunoprecipitated to quantify the levels of coprecipitated 7SK RNA in response to etoposide by qRT-PCR (means ± standard errors of the means; n = 3). (E) PPM1G is phosphorylated at Ser183 (S183) in response to etoposide, and an ATMi blocks site-specific PPM1G phosphorylation (pS183) upon etoposide treatment. HeLa cells were transfected with Strep-tagged WT PPM1G or the S183A mutant and treated as described above for panel D. Proteins were affinity purified and used for Western blot assays with the indicated antibodies. (F) PPM1G is phosphorylated by the ATM kinase at S183. Strep-affinity-purified WT PPM1G or the S183A mutant was incubated with (+) or without (−) ATM kinase, and Western blot analyses (total PPM1G and the pS183 form) were performed. (G) Mutation of the Ser183 residue (S183A) in PPM1G reduces the PPM1G-7SK RNA interaction in response to etoposide. HeLa cells were transfected with Strep-tagged WT PPM1G or the S183A mutant, treated with etoposide (+) or DMSO (−) for 30 min, and cross-linked with formaldehyde, and a RIP assay (X-RIP) was performed to quantitate the association between PPM1G and 7SK RNA by using qRT-PCR (means ± standard errors of the means; n = 3). (H) Mutation of Ser183 in PPM1G (S183A) reduces activation of IL-8 gene expression in response to etoposide. HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA-resistant (HS_PPM1G_6 [see Table S3 at http://www.utsouthwestern.edu/labs/dorso/research/lab-projects.html]) Strep-tagged WT PPM1G or the S183A mutant and retransfected 24 h later with a PPM1G siRNA to knock down endogenous PPM1G. Forty-eight hours later (at which time the PPM1G KD level was ∼80%), cells were treated with etoposide (+) or DMSO (−) for 120 min, RNA was extracted, and IL-8 gene expression was quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized to the β-actin level (means ± standard errors of the means; n = 3). (I) Strep-tagged WT PPM1G and S183A mutant proteins were affinity purified and visualized by Coomassie staining. MK, protein molecular size marker. (J) Gel shift assays with 7SK RNA and increasing amounts of WT PPM1G or the S183A mutant. (K) Binding curves for the gel shifts shown in panel J. (L) Determination of the kinetic parameters Km and Vmax for WT PPM1G, the S183A mutant, and the catalytically dead mutant (D496A) on the phosphatase substrate pNPP. (M) Purified P-TEFb was incubated with WT PPM1G or the S183A mutant under dephosphorylation conditions, and Cdk9 T-loop phosphorylation at Thr186 (pT186) was monitored by Western blotting. (N) The S183A mutation in PPM1G does not affect the enzymatic release of P-TEFb from the 7SK snRNP complex. 7SK-bound P-TEFb complexes were incubated with WT PPM1G or the S183A mutant under dephosphorylation conditions. Subsequent purification of P-TEFb using FLAG beads was done to monitor released (supernatant) and retained (pellet) components by Western blotting.