Figure 1.
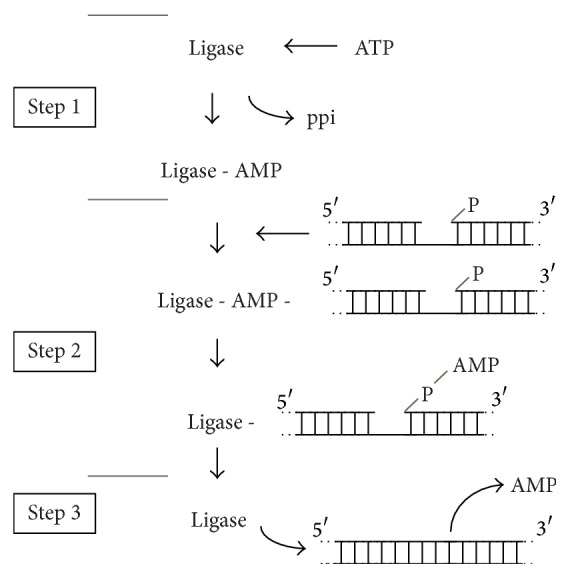
Schematic diagram of the three-step reaction catalyzed by ATP-dependent DNA ligases. The three-step reaction catalyzed by DNA ligase (Ligase) results in the serial transfer of AMP (adenosine 5′-monophosphate) to an active site lysine (step 1) and then to the 5′-PO4 end of DNA (step 2). During step 3, the 3′-OH end of a second DNA strand attacks the 5′-PO4, to release AMP and generate the ligated DNA product.
