Figure 1.
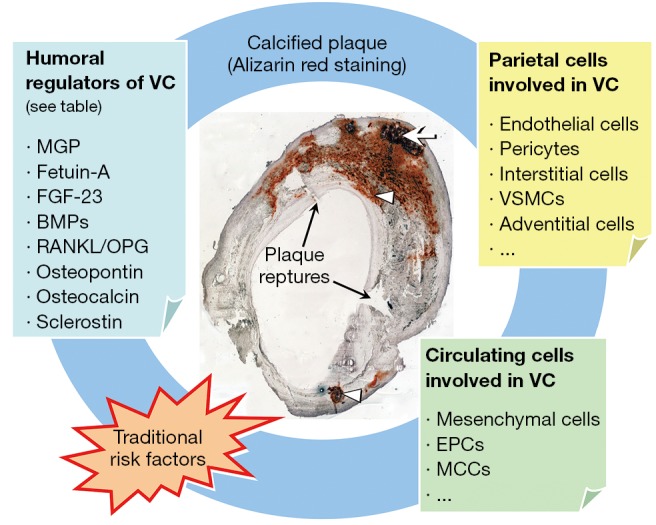
Contributors to plaque calcification. Representative Alizarin red staining of a carotid plaque section is shown with a calcified nodule (arrow) in the medial layer and other calcifications (arrowheads) beneath the endothelial layer; Plaque ruptures are also present where indicated. Multiple mechanisms contribute to plaque calcification and they are interacting mutually and with traditional risk factors. Humoral regulators, parietal as well as circulating cells are depicted. VC, vascular calcification; MGP, matrix Gla protein; FGF, Fibroblast growth factor; BMPs, bone morphogenetic proteins; RANKL, receptor activator for nuclear factor B ligand; OPG, osteoprotegerin; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cells; EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; MCCs, myeloid calcifying cells.
