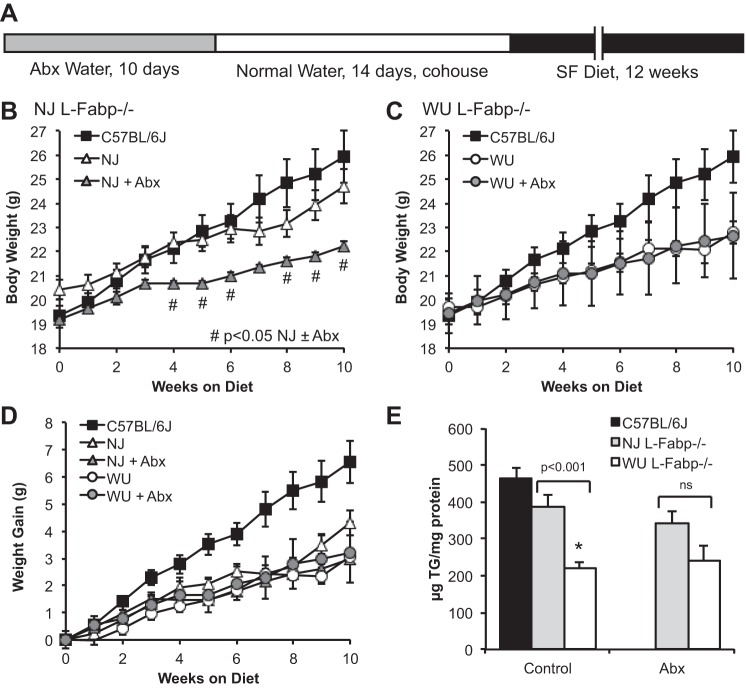
Fig. 5.
Antibiotic (Abx) treatment before SF feeding reduces differences in body weight and steatosis between NJ and WU L-Fabp−/− mice. A: schematic diagram showing Abx treatment protocol. B and C: average body weight of SF-fed NJ (B) and WU (C) L-Fabp−/− mice, with and without Abx pretreatment, shown relative to data from untreated C57BL/6J mice (from Fig. 3A) presented as a reference. #Significant differences between treated and untreated NJ L-Fabp−/− mice. D: weight gain of mice fed high-SF diet for 10 wk, with differences significant vs. untreated C57BL/6J for all L-Fabp−/− groups (±Abx) after 5 wk on the diet. E: hepatic TG content in Abx-treated mice. Note that differences in steatosis between NJ and WU L-Fabp−/− mice were reduced by Abx treatment. For Abx groups, n = 8 NJ L-Fabp−/− mice (F6) and 6 WU L-Fabp−/− mice (N9, F6). Values are means ± SE. *P < 0.001. ns, Nonsignificant.