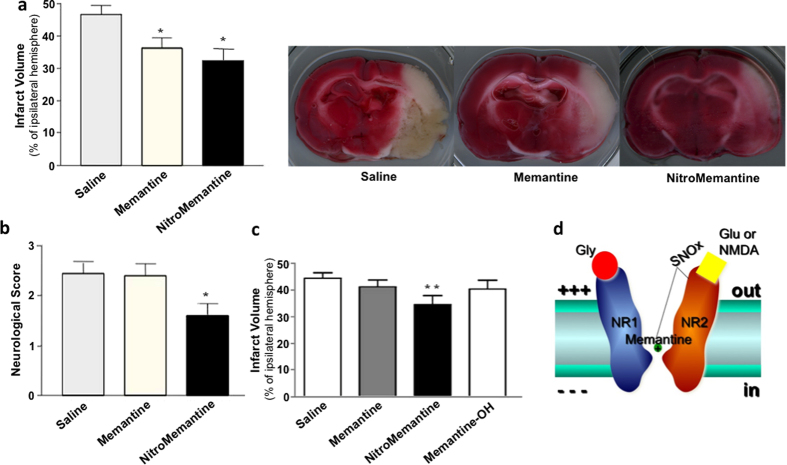
Figure 5. NitroMemantine protection and mechanism of action.
(a) NitroMemantine and memantine offer histological protection in the rat tMCAO/R model. Loading doses of drug (or saline control) were administered 2-h post occlusion, maintenance doses 12 h later, and animals sacrificed at 24 h. Left: A lower dose of YQW-036 (see text) protected to a greater extent than memantine, as assessed by 2,3,5-triphenyl-2H-tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining (*P < 0.05 by ANOVA with posthoc Scheffé). Right: Representative TTC-stained coronal brain sections under each treatment protocol. (b) NitroMemantine but not memantine showed a protective effect on objective neurological/behavioral testing (see Experimental Procedures, *P < 0.05 by ANOVA with posthoc Scheffé). Number of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats (SHR) tested in panels a and b: n = 9 for saline group; n = 4 for memantine-treated group; n = 5 for NitroMemantine-treated group. (c) NitroMemantine treatment reduced the size of infarct compared to memantine, memantine-OH, and vehicle controls (**P < 0.01 by ANOVA with posthoc Scheffé). Number of SHR tested: n = 13 for saline group; n = 10 for memantine-treated group; n = 8 for NitroMemantine-treated group; n = 7 for memantine-OH-treated group. Values are mean ± s.e.m. for each panel. (d) Schematic of NitroMemantine action. The adamantane moiety provides targeted delivery of an NOx group (where x = 1 or 2) to the NMDAR, providing two sites of antagonist action. First, an adamantane, such as memantine, enters and binds preferentially to excessively open NMDAR-coupled channels. Second, an NOx group reacts with the redox site(s), comprised of reactive thiol group(s), outside of the voltage field of the channel (modified from ref. 12).