Figure 4. In vivo epistasis analyses reveal IFT-A proteins function downstream of the Fz2-Arrow receptor complex and upstream of Arm/β-cat.
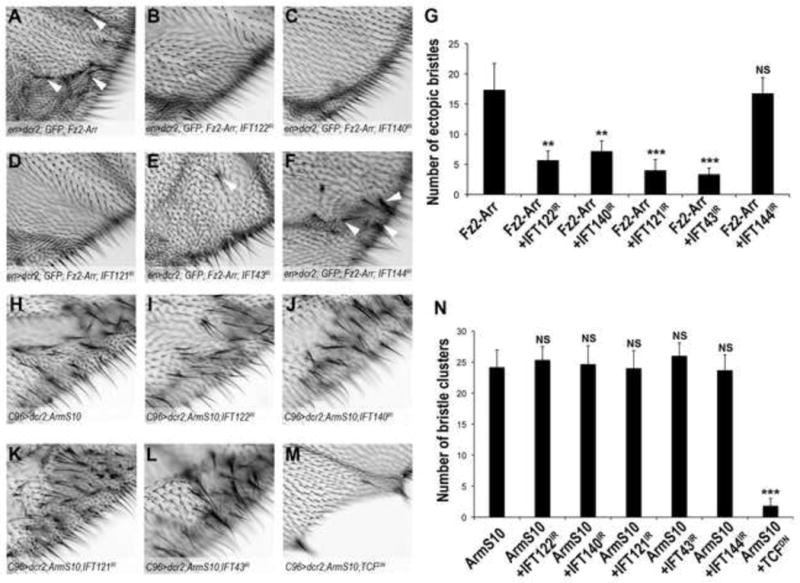
(A–G) High magnification view of extra margin bristle phenotype (examples indicated by white arrowheads) observed near margins of adult wings between L3 and L4 from flies expressing activated Fz2-Arr chimeric receptors (A) and Fz2-Arr combinations with IFT-A protein RNAi KD (B–F; genotypes are indicated in panels) under the control of enGal4 (image field as indicated in overview in Suppl. Fig. S4G). (G) Quantification of number of extra bristles/wing area shown, as induced by expression of Fz2-Arr (A) or Fz2-Arr and IFT-A KD factors (B–F) as indicated. All IFT-A KDs, except IFT144, suppress the extra- bristle phenotype. The bars represent mean SD, n≥10 fields per genotype, **= p<0.01 and ***= p<0.001, NS = non significant (student t-test).
(H–N) High magnification view of extra-margin bristles phenotype near margin of adult wings in C96>ArmS10 flies (image field as indicated in Suppl. Fig. S4M). (I–L) Co-expression of ArmS10 and RNAi against IFT-A components does not affect C96>ArmS10 phenotype (see also Suppl. Fig. S4N–S for whole adult wing images). (M) Co-expression of TCFDN suppresses C96>ArmS10 phenotype. (N) Quantification of number of extra bristles/wing area in the respective IFT-A protein KD backgrounds. The bars represent mean SD, n≥10 fields per genotype, ***= p<0.001, NS = non significant (student t-test).
See also Figure S4.
