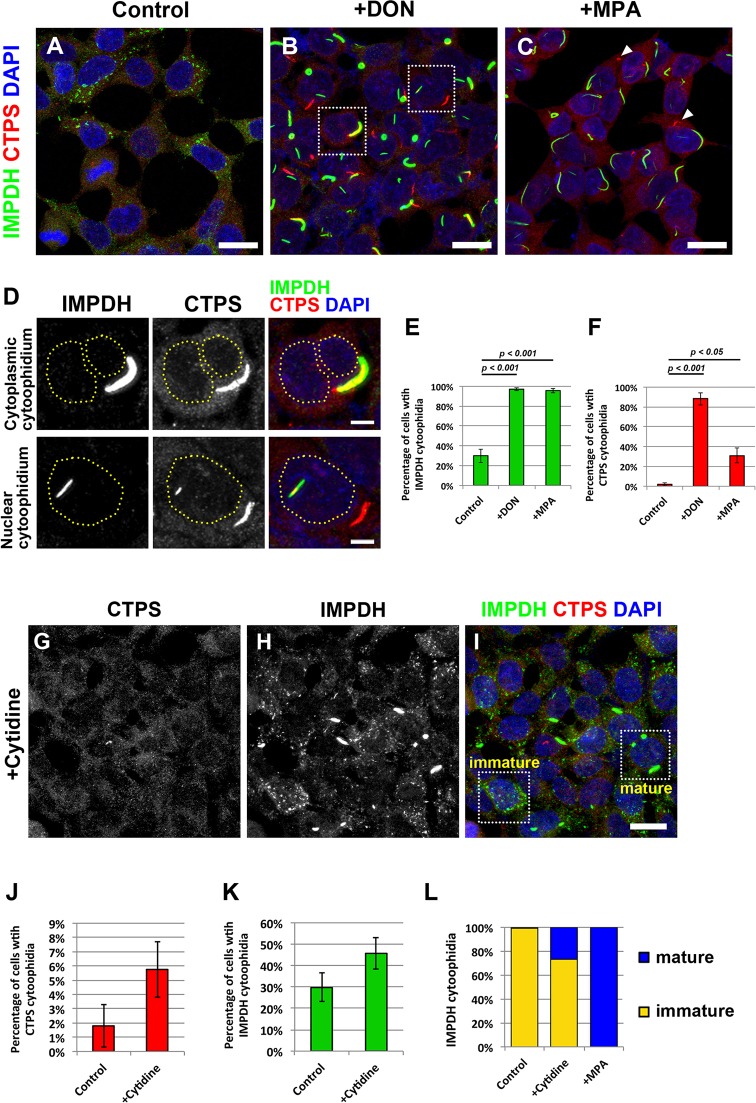
Fig. 1.
CTPS and IMPDH can form independent cytoophidium structures. Immunofluorescence of (A) untreated HEK 293T cells, and (B) HEK 293T cells treated with DON (10 μg/ml) or (C) MPA (10 μM) for 1 day before fixation. Arrowheads indicate CTPS cytoophidia. Scale bars: 20 μm. (D) Magnified views of the boxed areas in B showing colocalization of CTPS and IMPDH cytoophidia with the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Dashed lines indicate the outline of the nuclei. Scale bar: 5 μm. (E,F) Mean±s.e.m. percentages of cells with IMPDH and CTPS cytoophidia. P-values were calculated with a Student's t-test. (G–I) Immunofluorescence of HEK 293T cells cultured in medium with 100 μM cytidine for 1 h before fixation. Mature and immature IMPDH cytoophidia are shown in the selected areas in I. (J,K) Mean±s.e.m. percentages of cells with CTPS and IMPDH cytoophidia. There is no significant difference between the control and cytidine-treated group (Student's t-test, P values=0.16 and 0.19). (L) Ratios of mature and immature IMPDH cytoophidia observed in cells cultured under normal culture conditions (control), treated with 100 μM cytidine for 1 h (+cytidine), and treated with 10 μM MPA for 1 day (+MPA).