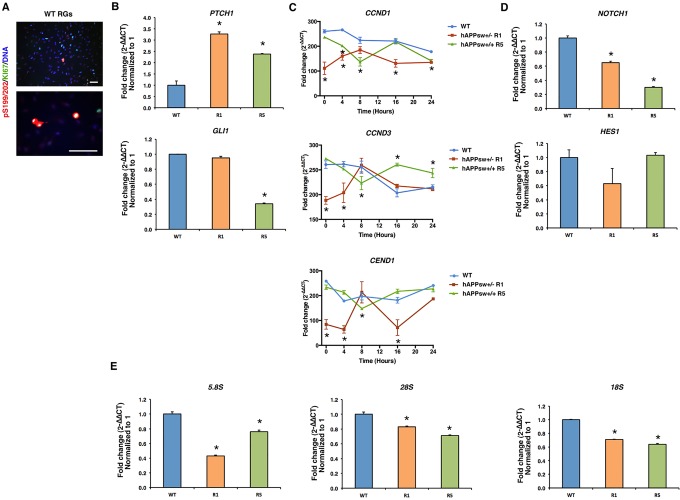
Fig. 5.
Genes associated with SHH signaling, the cell-cycle, NOTCH signaling and ribosomal RNA synthesis are dysregulated in hAPPsw RGs. (A) Expression of hyperphosphorylated pSer199/202 tau occurs in conjunction with mitotically dividing WT RGs (KI67+) and is therefore a normal process occurring during cell division. Magnification: 16× and 40×; scale bar: 100 µm. (B) Evaluation of the genes involved in SHH signaling show an increased expression of PTCH1 in hAPPsw RGs; however, the downstream marker GLI1 is decreased in hAPPsw+/+ RGs compared with WT. Student's t-test was performed on biological replicates and significance was found when P≤0.05 (marked by *). (C) Cell synchronization was performed to assess the expression of Cyclin D genes and CEND1 over 24 h. Cyclin D1 (CCND1) was significantly decreased in the hAPPsw RGs and altered expression of Cyclin D3 (CCND3) was observed at varying time points for the hAPPsw RGs. CEND1 was mostly decreased in the hAPPsw+/− RGs compared with WT RGs. Student's t-test was performed on biological replicates and significance was found when P≤0.05 (marked by *). (D) Expression of NOTCH signaling genes revealed a decrease in NOTCH1 in the hAPPsw RGs but no change was observed in expression of HES1. Student's t-test was performed on biological replicates and significance was found when P≤0.05 (marked by *). (E) Expression of the ribosomal RNA subunits 5.8S, 18S and 28S was significantly reduced in hAPPsw RGs compared with the WT RGs. For all comparative qPCR, Student's t-test was performed on three biological replicates and significance was found when P≤0.05 (marked by *).