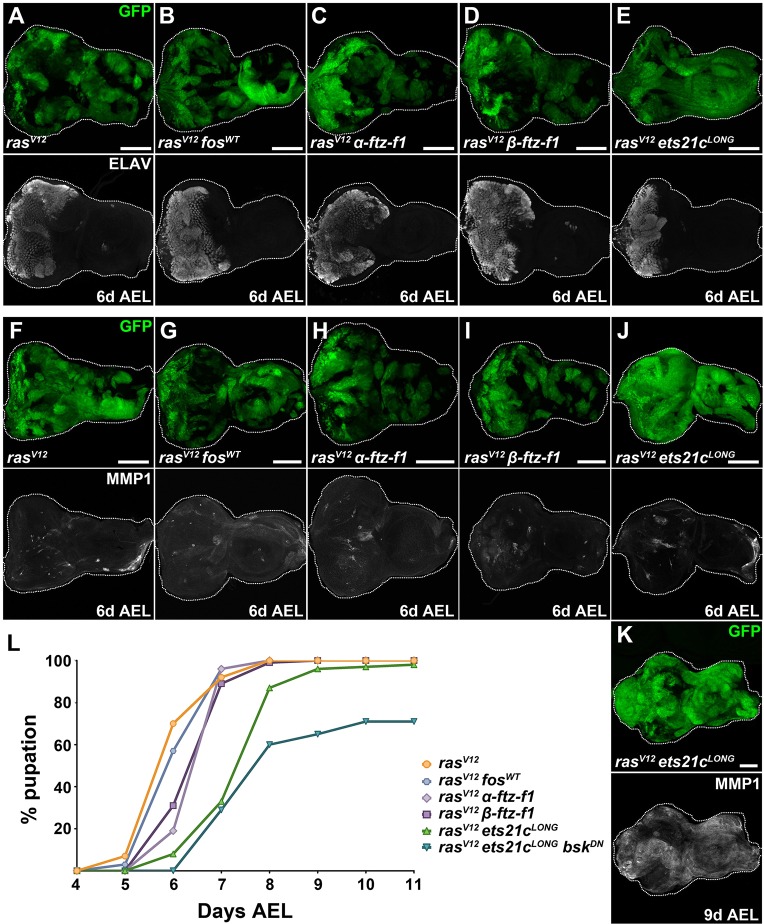
Fig. 5.
Ets21c cooperates with RasV12 to promote tumor growth, increase MMP1 expression and delay development. (A-K) Co-expression of rasV12 with ets21cLONG caused noticeable expansion of the GFP+ clonal area in EAD already on day 6 AEL (E,J). Nevertheless, photoreceptor differentiation marked by ELAV still occurred (E). Neither fosWT nor α- or β-ftz-f1 overexpression was sufficient to enhance clonal tumor growth when combined with rasV12 (B-D). Similar to rasV12 mosaic EAD (F), clones co-expressing rasV12 with fosWT (G), α-ftz-f1 (H), β-ftz-f1 (I) or ets21cLONG (J) showed only moderate enhancement of MMP1 levels on day 6 AEL. On day 9 AEL, rasV12ets21cLONG clones showed massive enrichment of MMP1 signal (K). Images show EAD as projections of multiple confocal sections. Scale bars: 100 µm (A-K). (L) rasV12α-ftz-f1 and rasV12β-ftz-f1 larvae pupated slightly later compared with rasV12 alone or rasV12fosWT (P<0.0001). In contrast, pupation of rasV12ets21cLONG larvae was delayed by 2 days (P<0.0001). Inhibition of JNK (rasV12ets21cLONGbskDN) further exacerbated the delay, arresting 29% of the tumor-bearing animals at the larval stage (P<0.0001). The graph shows the cumulative percentage of pupae forming over time.