Fig. 6.
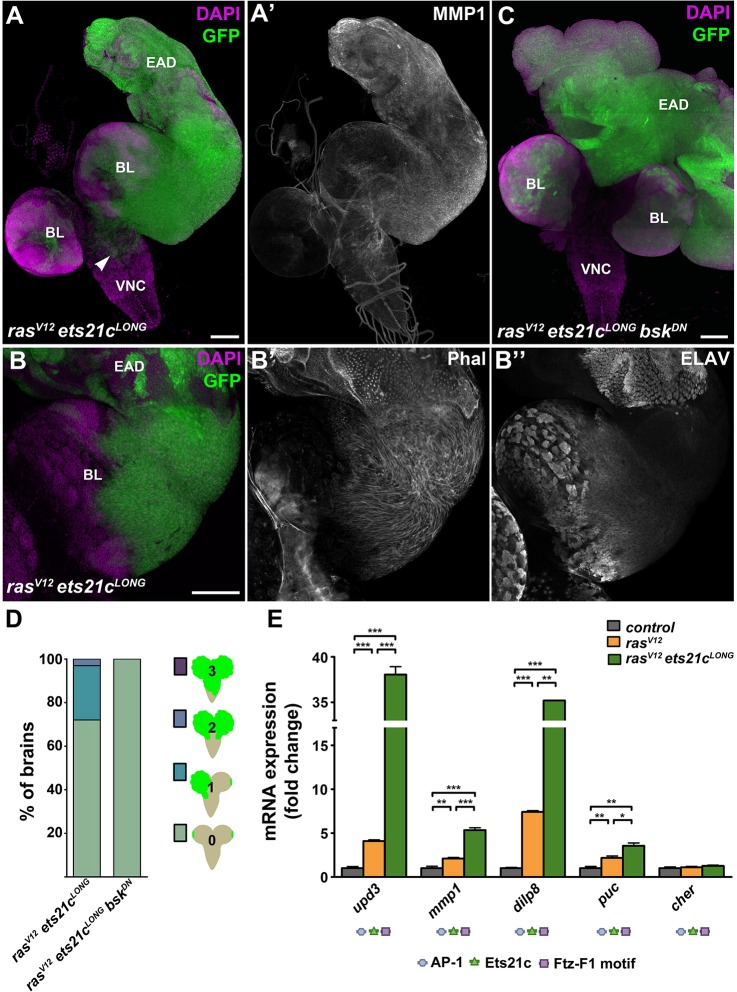
Ets21c requires JNK activity to promote invasiveness but not growth of tumors. (A-B) On day 9 AEL, rasV12ets21cLONG GFP-marked clones showed dramatic enrichment of MMP1 protein (A′) and filamentous actin, visualized with phalloidin (Phal; B′) in the cell cortex. Migrating cells were devoid of the differentiation marker ELAV (B″). rasV12ets21cLONG cells overgrew the entire EAD and spread over the brain lobes and VNC (arrowhead in A). (C) Blocking JNK (rasV12ets21cLONGbskDN) suppressed tumor invasiveness but caused even greater overgrowth of GFP+ clonal tissue within the EAD. (D) Quantification of tumor invasiveness confirmed the requirement of JNK signaling for dissemination of rasV12ets21cLONG clonal cells. Four grades of invasiveness were scored based on spreading of clonal GFP-positive cells into larval brains dissected on day 8 AEL. Results are the percentage of brains in each category with P<0.0001. (E) rasV12ets21cLONG mosaic EAD showed marked increase in expression of the JNK targets upd3, mmp1, dilp8 and puc, whereas cher expression was unaffected relative to control and rasV12 mosaic EAD. Data are mean values±s.e.m.; n=3-5; ***P<0.001; **P<0.005; *P<0.01. Regulatory regions of all tested genes harbor AP-1, Ets21c and Ftz-F1 binding motifs. (A,C) show projections of multiple confocal sections, and (B) represents single sections. Scale bars: 100 µm (A-C). EAD, eye/antenna disc; BL, brain lobe; VNC, ventral nerve cord.