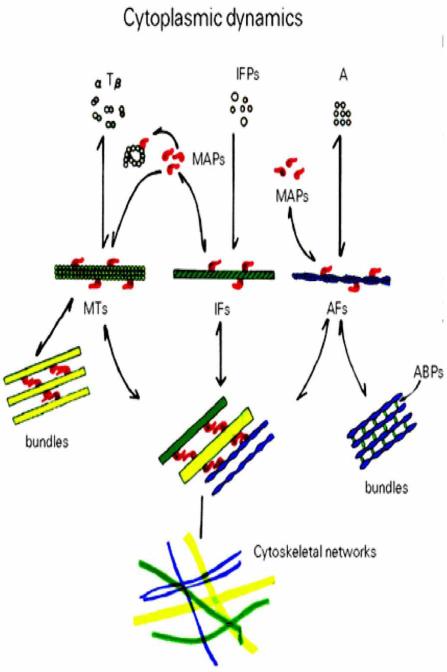
Fig. (13).
A scheme showing the assembly of macromolecular units into cytoskeletal polymers, and their association into various supramolecular structures, such as filaments or bundles. Note that microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) and actin-binding proteins (ABPs) are required for a proper assembly of these supramolecular structures that include microtubules (MTs), intermediate filaments (IF) and actin filaments (AFs). Many peptide assemblies and tertiary structures, including the pathological conformations of prions, could not be, therefore, reproduced in vitro, out of their native, intracellular environments owing to their proper assembly or conformational change being preconditioned by the co-assembling activity of other molecular species. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [84].