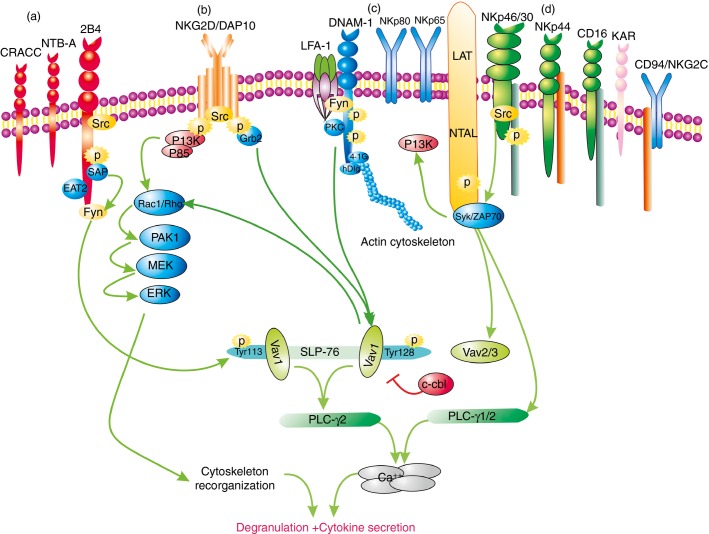
Figure 2.
Multiple activating human natural killer (NK) cell receptors and representative signalling pathways of 2B4, NKG2D, DNAM-1 and NKp46/30. (a) SLAM family receptor CRACC (CD319), NTB-A (CD84), and 2B4; e.g. 2B4 transduces signal in ITSM-SAP/EAT-2-Fyn-dependent pathway. (b) NKG2D; e.g. NKG2D/DAP10 transduces signal in DAP10-PI3K-MAPK/Grb2-Vav1-dependent pathway. (c) DNAM-1, NKp80, and NKp65; e.g.DNAM-1 signalling cascade is described in text. (d) NKp46/NKp30, NKp44, CD16 (FcγRIIIA), KAR and CD94/NKG2C. e.g.NKp46/NKp30 transduces signal in ITAM-Syk/ZAP70-dependent pathway, and results in subsequently activation of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K), Vav2/3 and phospholipase C (PLC)-γ1/2. The first step to transduce intracellular signal of all activation receptors is to be phosphorylated by Src family kinases. 2B4 can induce Src homology 2(SH2) domain-containing leucocyte phosphoprotein of 76 000 MW (SLP-76) phosphorylation at Tyr113, whereas NKG2D and DNAM-1 can only induce SLP-76 phosphorylation at Tyr128. Two Vav1, which could inhibit degradation by the E3 ubiquitin ligase c-cbl, bind to two phosphotyrosines of SLP-76 and result in synergistic activation of NK cells. All activation receptors induce ultimately PLC-γ1/2 activation, Ca2+ flux, cytoskeletal reorganization, and result in degranulation and cytokine secretion. SLAM, signalling lymphocytic-activation molecule; ITSM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif; SAP, SLAM-associated protein; EAT2, Ewing-sarcoma-associated transcripts 2; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; Grb2, grow factor binding protein 2; Syk, spleen tyrosine kinase; ZAP, ζ chain-associated protein kinase; LFA-1, lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; LAT, linker for the activation of T cells; NTAL, non-T-cell activation linker.