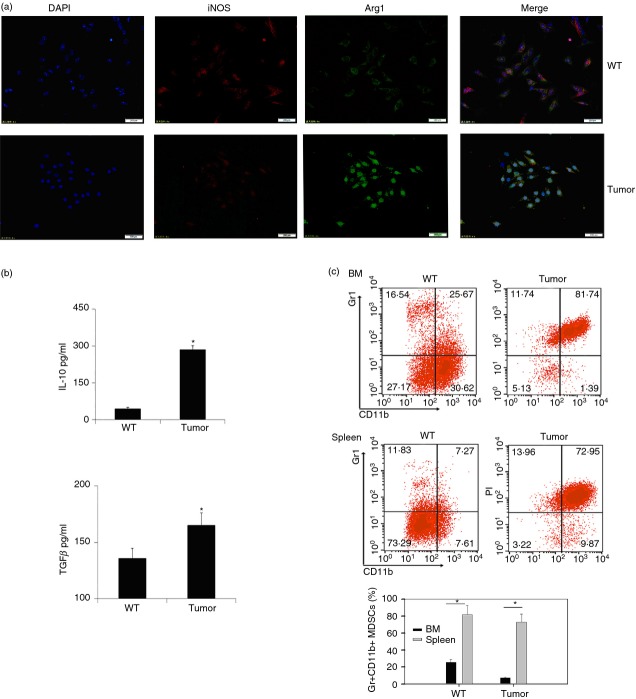
Figure 1.
Gr-1+ CD11b+ monocytes exhibited an M2 phenotype in tumour-bearing mice. (a) Gr-1+ CD11b+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) purified from wild-type (WT) and tumour-bearing mice were stained with anti-inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; red) and anti-Arginase 1 (Arg1; green) fluorescent antibody and analysed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (b) Concentration of interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) of Gr-1+ CD11b+ monocytes in spleen of normal C57BL/6 mice (indicated as WT) or tumour-bearing mice (indicated as tumour) were detected by ELISA. Data are representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0·05, Student's t-test. (c) Percentages of Gr-1+ CD11b+ monocytes in bone marrow and spleen were assayed by flow cytometry. Cells were prepared on a Percoll density gradient as described in the Materials and methods, and stained with anti-Gr1 and anti-CD11b antibodies. Percentages of Gr-1+ CD11b+ MDSCs were stained as described in (c) (upper) for flow cytometric analysis. *P < 0·05, Student's t-test. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments (b, c).