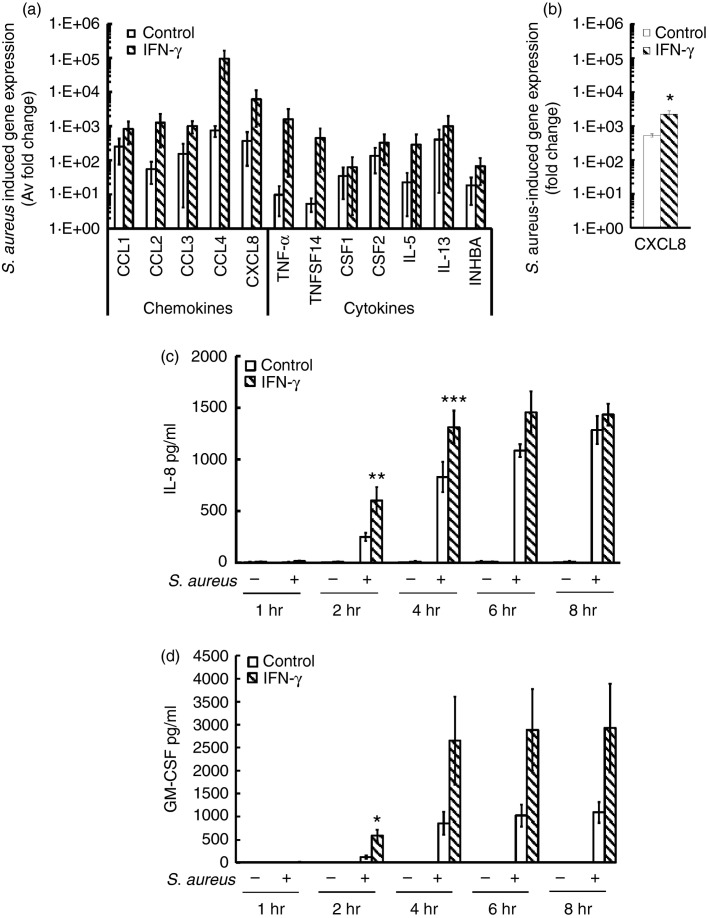
Figure 5.
Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) enhances Staphylococcus aureus-dependent CXCL8 and granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) secretion by human mast cells (huMCs). Human MCs were pre-treated with IFN-γ (20 ng/ml) for 48 hr before the addition of S. aureus (20 : 1). After 2 hr, mRNA was isolated, cDNA was transcribed and quantitative PCR was performed for analysis of cytokine and chemokine induction by S. aureus using a SuperArray platform (a) or real-time PCR (b). For quantification of CXCL8 and GM-CSF protein release, cell-free supernatants were collected after 1–8 hr and quantified for CXCL8 (c) and GM-CSF (d) by ELISA. Results are average fold change in mRNA levels relative to huMCs without bacterial exposure (a, b) or means ± SE performed in duplicate (c, d), n = 3–4 separate huMC donors. Differences between individual groups were tested for statistical significance by two-way repeated measures analysis of variance with Holm–Sidak correction for multiple comparisons (*P ≤ 0·05; **P > 0·01; ***P > 0·001 for comparison between control and IFN-γ-stimulated cells exposed to S. aureus).