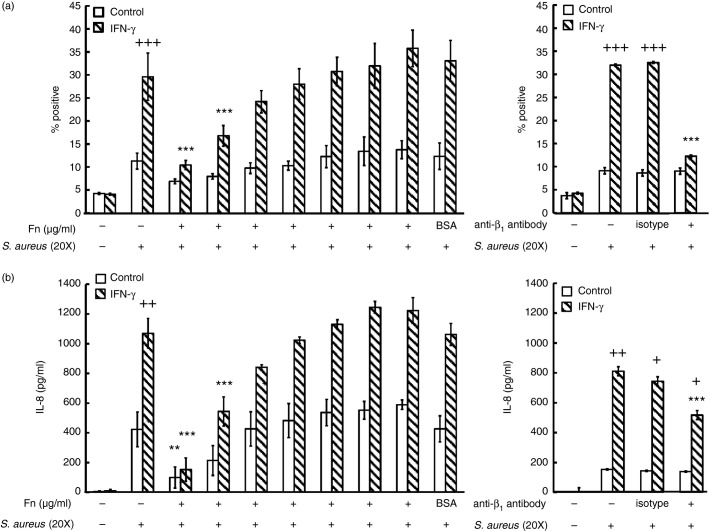
Figure 9.
Blockade of integrin receptors on human mast cells (huMCs) reduces Staphylococcus aureus-dependent binding and CXCL8 secretion. Human MCs were incubated with IFN-γ for 48 hr before a 1-hr exposure to increasing concentrations of fibronectin (1–100 μg/ml) or β1 integrin blocking antibody. Binding of FITC-SA was analysed by flow cytometry after 1 hr at 4° (a) or S. aureus-induced CXCL8 secretion in cell-free supernatants after 2 hr at 37° (b) was then determined. Results are means ± SE performed in duplicate, n = 3 or n = 4 huMC donors. Differences between individual groups were tested for statistical significance by two-way repeated measures analysis of variance with Holm–Sidak correction for multiple comparisons (+P < 0·05; ++P ≤ 0·01; +++P ≤ 0·001 for comparison between control and IFN-γ-stimulated cells and *P < 0·05; **P ≤ 0·01 and ***P ≤ 0·001 for comparison with S. aureus-treated cells).