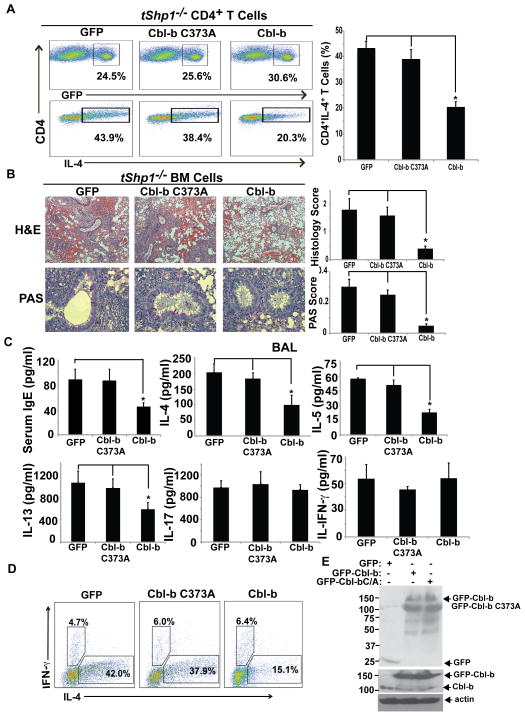
FIGURE 6.
Over-expression of Cbl-b in T cells inhibits heightened Th2 response in tShp1−/− mice. (A) Naïve CD4+CD25− T cells from tShp1−/− mice were transfected with HA-tagged Cbl-b or Cbl-b C373A mutant by retroviral infection, and cultured under Th2-biased condition. Three days later, the cells were surface-stained with anti-CD4, and intracellularly stained with anti-IL-4 and anti-IFN-γ. (B) Bone-marrow cells from tShp1−/− mice were transfected with GFP-tagged Cbl-b or Cbl-b C373A mutant, and injected into lethally-irradiated Rag1−/− mice. Eight weeks later, the recipients were immunized with OVA in alum, challenged at day 21 for three consecutive days, and sacrificed on day 24. Lung histology was determined by H&E and PAS staining. (C) IgE in the serum and cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and IFN-γ) in the BAL fluid were determined. (D) The spleen cells from B were surface-stained with anti-CD4, and intracellularly stained with anti-IL-4 and anti-IFN-γ. (E) T cell lysates from irradiated Rag1−/− mice receiving tShp1−/− BM cells overexpressing HA-Cbl-b-GFP, HA-Cbl-b C373A-GFP or a control empty vector were blotted with anti-GFP, anti-Cbl-b, and anti-actin, respectively. Data are representative of two independent experiments. *p<0.05; Student t test.