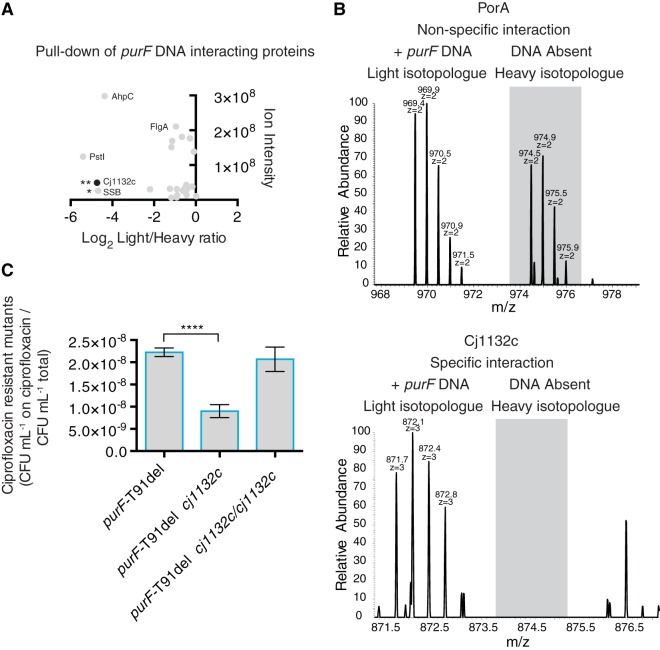
FIG 7 .
SILAC-based affinity capture of Cj1132c with purF DNA bait and effect of cj1132c deletion on spontaneous mutation rate. (A) Screen for DNA-binding proteins captured with purF DNA bait. Differentially labeled (light, [13C6]arginine, or heavy, [13C614N4]arginine) C. jejuni total protein lysates were incubated with biotinylated purF DNA or prsA DNA, respectively. A 1:1 light/heavy mixture of DNA/protein complexes was captured on streptavidin beads. Proteins were eluted from beads by digestion with PstI restriction enzyme, and trypsinized proteins were analyzed by gel electrophoresis liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Each dot represents an identified peptide. SILAC analysis discriminates the specificity of an interaction; peptides with a low heavy/light ratio indicate higher-affinity capture. Data are representative of two independent experiments statistically assessed by the Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR), and FDR Q significance values are indicated: *, Q = 0.024; **, Q = 0.014. (B) Representative mass spectra for SILAC-labeled captured peptides. Top, equal mass/charge ratio of light and heavy forms of PorA peptide indicating nonspecific interaction; bottom, the light form of Cj1132c is present in a ratio >16.8 times higher than the heavy form, indicating a high probability of interaction with the direct repeat and hypervariable region of purF. (C) Frequency of emergence of spontaneous ciprofloxacin resistance (spontaneous mutation rate) of Δcj1132c and complemented Δcj1132c/cj1132c mutants in purF-T91del genetic background. The numbers of spontaneous ciprofloxacin-resistant mutants relative to total CFU per OD600 equivalent are presented. Mean results with SEM from six independent experiments each with two technical replicates are shown: ****, P ≤ 0.0001.