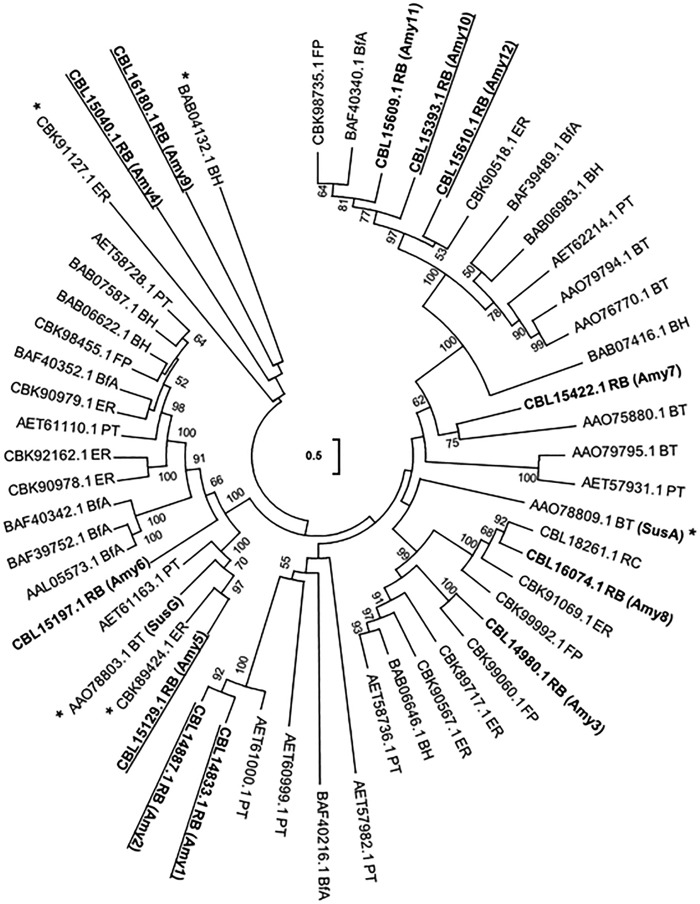
FIG 2 .
Phylogenetic tree comparing GH13 enzymes from Ruminococcus bromii and seven other bacterial genomes. R. bromii L2-63 (RB) GH13 sequences (labeled Amy1, Amy2, Amy3, etc.) are compared with those from other human gut species (the starch-utilizing strains Eubacterium rectale A1-86 [ER], Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 [BT], and Bifidobacterium adolescentis ATCC15703 [BfA] and two other human colonic Ruminococcaceae species, Ruminococcus champanellensis 18P13 [RC] and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii L2-6 [FP]) and also with those from two non-gut species, Bacillus halodurans C-125 (BH) and Paenibacillus terrae HPL-003 (PT), that were known from the results of BLASTp queries of the NCBI database to possess proteins that were the closest matches to R. bromii Amy4. R. bromii sequences that are predicted to possess signal peptides are underlined. Sequences with functions concerned with glycogen or trehalose metabolism (including R. bromii L2-63 Amy 13, Amy14, and Amy15) that are predicted by KEGG GH annotation have been omitted from the tree. Sequences marked with an asterisk (*) encode enzymes that have been experimentally characterized. Bootstrap values, expressed as a percentage of 1,000 replications, are given at the branching nodes. This tree is unrooted and was constructed using the maximum-likelihood method. The scale bar (center of tree) refers to the number of amino acid differences per position.