Figure 1.
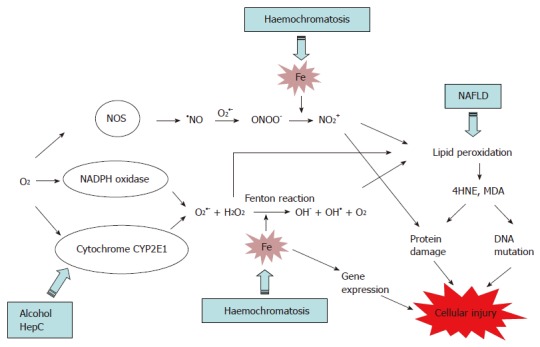
The involvement of iron in oxidative stress and its cytotoxic conse-quences. Iron catalyses the production of the reactive molecules OH• (via the Fenton reaction) and NO2+, which promote lipid peroxidation and protein damage leading to cellular injury. NOS, nitric oxide synthase; •NO, nitric oxide; ONOO-, peroxynitrite; O2•-, superoxide radical; OH•, hydroxyl radical; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; NO2+, nitronium anion; Fe, iron; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
