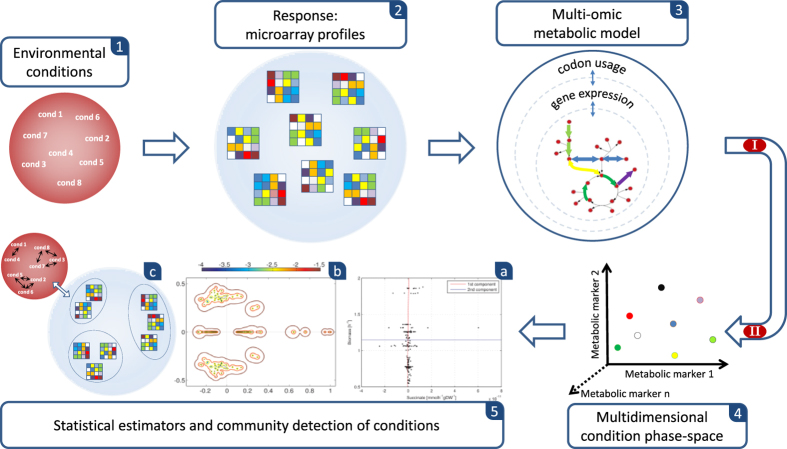
Figure 1. Pipeline of METRADE (MEtabolic and TRanscriptomics ADaptation Estimator).
The idea behind the methods proposed in this study is that an accurate prediction on the relations among conditions should not disregard a multi-omic model to associate conditions to a phenotypic outcome in a set of objective spaces; indeed, a multi-omic inference cannot be performed by looking only at the gene expression profiles associated with the conditions, but requires a mapping to the phenotype that estimates the actual effect of each condition on the bacterial physiology. (See Discussion for further comments on the rationale behind METRADE.). Part I (panels 1–3). The response to environmental conditions (1) in which E. coli is grown (e.g., low or high glucose, aerobic or anaerobic, pH changes, antibiotics, heat shock) is measured through Affymetrix Antisense2 microarray expression profiling (2). To evaluate the environmental conditions and detect their community structure, we derive a multi-omic model (3) of the E. coli metabolism, taking into account gene expression and codon usage. Part II (panels 4,5). (4) The model is able to account for multiple growth conditions and temporal multiobjective evolution towards the production of selected metabolites through the Pareto front. It is also able to associate each environmental condition with a single point in a multidimensional condition phase-space. The adaptability to one condition is given by the time evolution of the bacterial genome, which can be estimated by the hypervolume indicator. (5) We use a set of statistical estimators defined on our multi-omic model with the aim of analyzing the adaptability to experimental conditions. We apply the principal component analysis (5a) to the condition space in order to investigate the directions with largest variance, the pseudospectrum and its bagplot (5b) to shed light on the structure of a distance matrix built on the condition phase-space, and a spectral method for community detection to infer condition similarities (5c) according to the E. coli response in the multiobjective space.