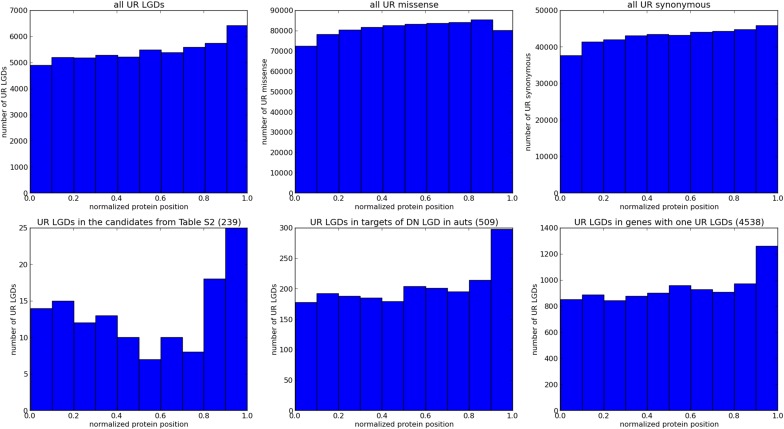
Fig. S1.
Amino acid positions. Shown are the normalized amino acid codon positions for six classes of UR variants. The normalized positions are computed as the position of the affected amino acid divided by the length of the encoded protein, using as a reference the isoform that encodes the longest protein. (Top) Histograms of the normalized positions for all UR LGD, missense, and synonymous variants. (Bottom) Histograms of the positions for three subsets of the UR LGD variants: the set of UR LGD variants found in the top 239 genes based on the heuristic posterior score (Dataset S2), the set of UR LGD variants found in the targets of DN LGD mutation in affected autistic (auts) children (509 genes), and the set of UR LGD variants found in genes with exactly one UR LGD variant (4,538 genes). Whereas the normalized amino acid positions of the UR missense and synonymous variants are fairly uniformly distributed across the length of the protein, there is a marked increase in UR LGD variants toward the regions encoding the C-terminal ends of the proteins. This increase is more pronounced for the sets of vulnerable genes shown in the bottom row.