Fig. 1.
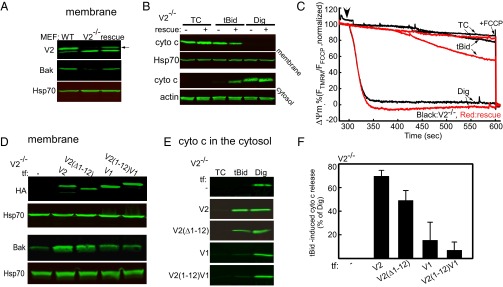
Genetic rescue studies in V2−/− MEFs. Unique N-terminal extension in V2 is neither necessary nor enough for Bak import and cyto c release. (A) Western blot verification of the presence of V2 and Bak in the membrane fraction of WT and V2−/− cells rescued with avV2. The arrow shows the relevant band of V2. (B) Cyto c release was monitored by detecting the cyto c level in the membrane and cytosolic fraction of nonrescued (−) and avV2-rescued (+) V2−/− permeabilized MEFs 5 min after treatment with solvent [tBid (25 nM) or digitonin (Dig, 600 μg/mL)]. TC, time control. Hsp70 and actin were used as loading controls. (C) Representative traces for the time course of ΔΨm recorded in cell suspensions using a fluorometer. The experiment was carried out in permeabilized V2−/− (black line) or avV2-rescued V2−/− (red line) cells treated with tBid or Dig (added at 300 s, marked by an arrow). FCCP (5 μM) was added at the end of the recordings to dissipate the remaining ΔΨm. Data are presented as the percentage of the initial ΔΨm. TCs are the nontreated samples. (D) HA and Bak Western blot of the membrane fraction of V2−/− cells transfected (tf) with HA-tagged V2, V2(Δ1–12), V1, or V2(1–12)V1. Immunoblot (E) and quantitative analysis (F) of cyto c in the cytosolic fraction of V2−/− cells transfected with V2, V2(Δ1–12), V1, or V2(1–12)V1 and treated with tBid or Dig after plasma membrane permeabilization. In response to tBid, the cyto c band was normalized to the response to Dig in each condition (n = 3).
