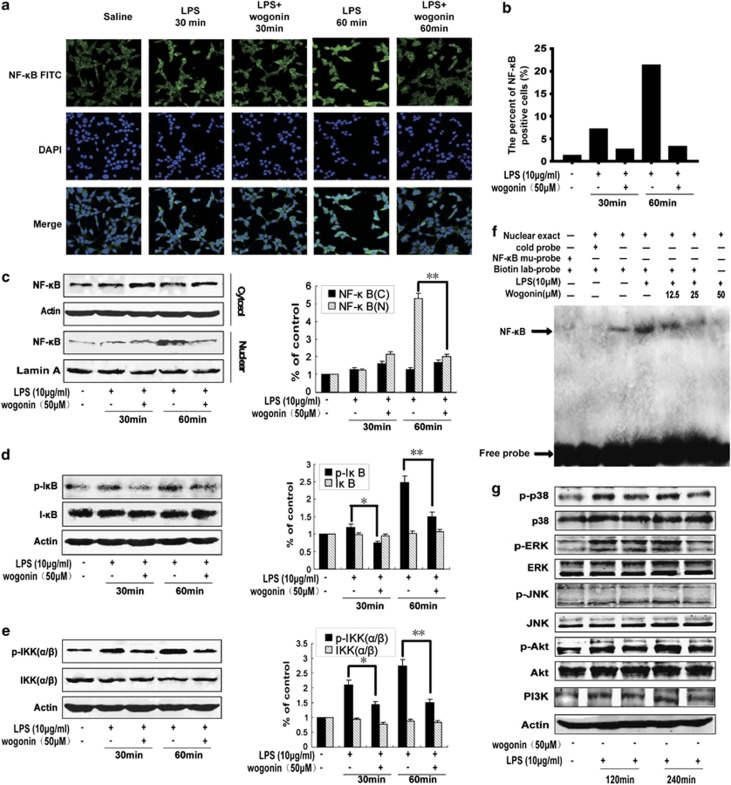
Figure 4.
Effect of wogonin on LPS-induced activation of NF-κB signaling pathway in HCT116 cells. (a) Immunofluorescence was performed to analyze NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation. (b) The percentage of cells with NF-κB translocation to the nucleus was shown. (c) Western blotting was performed to analyze NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation. Lamin A and β-actin were used as nuclear and cytoplasmic markers, respectively. Whole-cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting using various antibodies against p-IκBα (d) and p-IKK (e). Experiments were repeated three times with similar observations in each experiment. Densitometric analysis was performed to determine the relative ratios of each protein. All data are expressed as the mean±S.D., *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus LPS group. (f) Nuclear extracts were prepared and subjected to EMSA to detect NF-κB activation. Arrowhead indicates the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB. Binding is competed by unlabeled NF-κB oligonucleotides (cold) and shifted by the addition of a p65 antibody. (g) Effects of wogonin on the LPS-induced PI3K and MAPK signaling pathway components. HCT116 cells were treated with 50 μM wogonin for 120 and 240 min before the addition of 10 μg/ml LPS