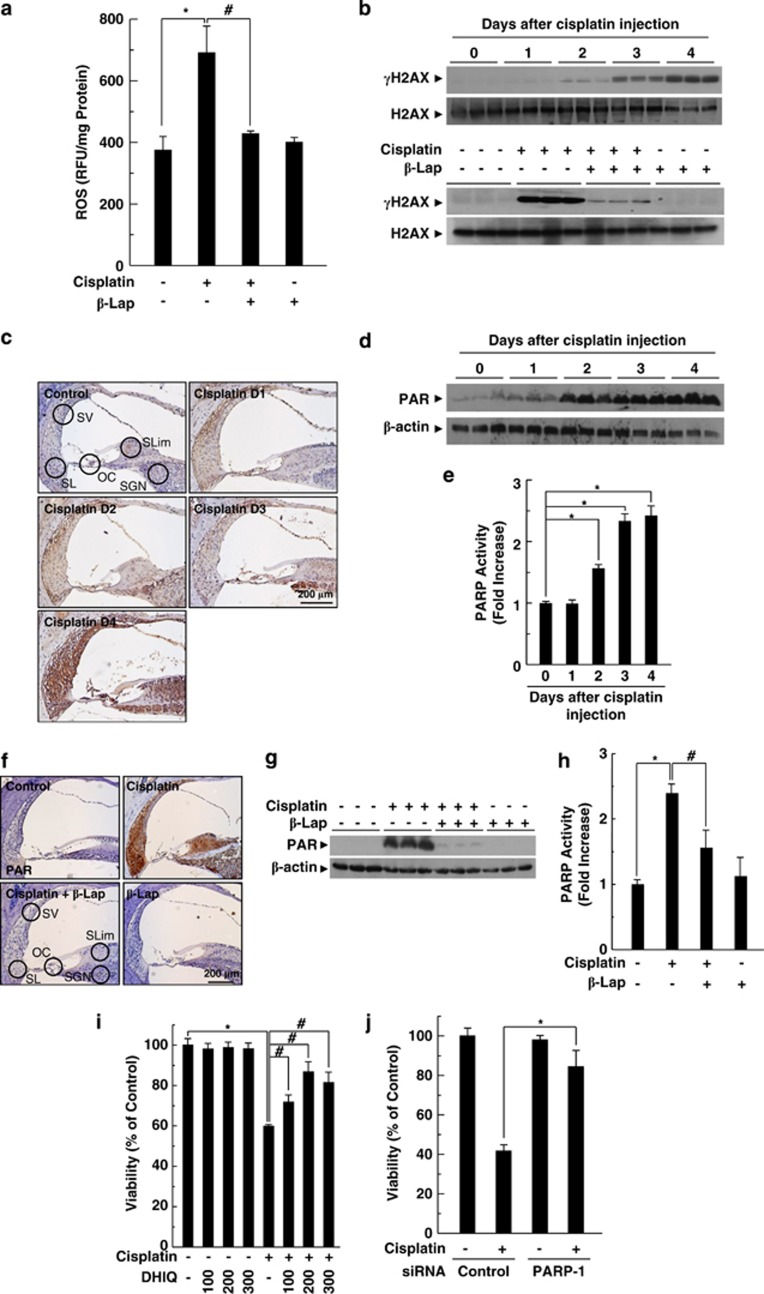
Figure 3.
PARP-1 activation in cisplatin ototoxicity. β-Lap (40 mg/kg body weight) was administered orally once a day for 4 consecutive days. Cisplatin (16 mg/kg body weight) was injected once at 12 h after the first β-Lap administration. (a) Cochlear tissue was isolated at 4 days after cisplatin injection, and then tissue extracts were incubated with 20 μM of 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate to determine total ROS at 37 °C for 60 min. Fluorescence intensity was recorded using a fluorometer and normalized to protein content. (b) Cochlear tissue was isolated at indicated times (upper) and 4 days (lower) after cisplatin treatment. (c–h) DNA damage was determined by western blotting using anti-γH2AX antibody. PARP-1 activation was analyzed by IHC (c and f) and western blotting (d and g) using anti-PAR antibody, and PARP activity was assayed using the PARP assay kit (e and h) in the cisplatin-treated cochlear tissue. Control, PBS-treated group; Cisplatin, 16 mg/kg cisplatin only group; Cisplatin+β-Lap, cisplatin and 40 mg/kg β-Lap combined group; β-Lap, 40 mg/kg β-Lap only group. *,#P<0.05 by one-way ANOVA compared with the control (*) and cisplatin only (#) group, (n=5). (i and j) HEI-OC1 cells were pretreated with the indicated doses of DHIQ for 30 min (i) or transfected with 100 nM control or PARP-1-specific siRNAs for 24 h (j), and then further maintained in 20 μM cisplatin for 24 h. The cell viability was measured by MTT assay. *,#P<0.05 by one-way ANOVA compared with the control (*) and cisplatin only (#) group, (n=3). OC, organ of Corti; SGN, spiral ganglion neuron; SL, spiral ligament; SLim, spiral limbus; SV, stria vascularis