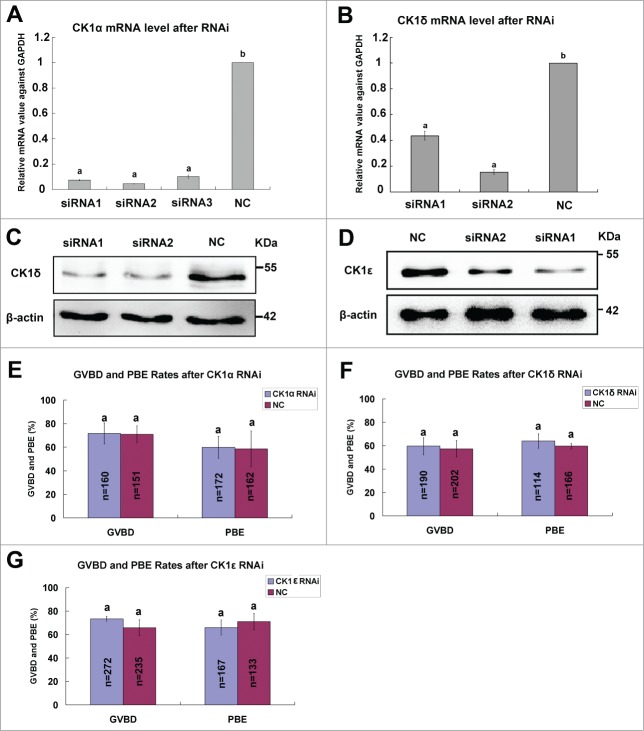
Figre 4.
Individual effect of CK1α, CK1δ or CK1ϵ knock down on oocyte meiotic progression. Oocytes at GV stage were microinjected with siRNAs (30 μM) against CK1α, CK1δ and CK1ϵ, respectively. The same amount of negative control siRNA (NC) was injected as control. After 24 hours of arrest at GV stage, oocytes were collected and used for RNAi efficiency measurement at mRNA level or protein level. (A, B) The knockdown efficiency of CK1α and CK1δ siRNAs at mRNA level. The relative mRNA level of CK1α (A) or CK1δ (B) compared to NC group was measured by real-time quantitative PCR. Different superscript letters indicate statistical difference (p < 0.05). (C, D) Western blot analysis showed the knockdown efficiency of CK1δ (C) and CK1ϵ (D) siRNAs at protein level. A total of 100 oocytes were collected per sample. (E-G) 30μM CK1α-siRNA2 (E), CK1δ-siRNA2 (F) and CK1ϵ-siRNA1 (G) was microinjected into GV oocytes, respectively. The same amount of NC siRNA was microinjected as control. After 24 hours arrest at GV stage, oocytes were released to fresh M16 medium and cultured for 14 hours. The GVBD rates and PBE rates were calculated, respectively. Data are presented as mean±s.e.m. The same superscript letters indicate no statistical difference (p > 0.05).