Fig. 7.
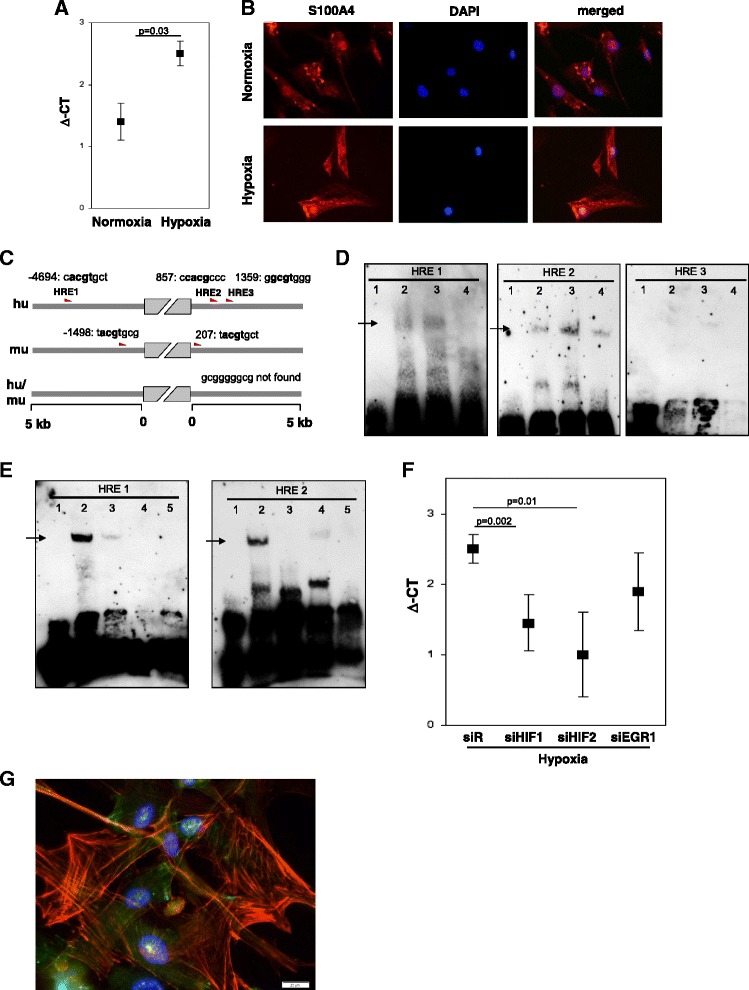
Hypoxia-dependent S100A4 expression in human primary pulmonary arterial cells. a Real-time analysis of S100A4 expression in human PASMC after normoxia and hypoxia exposure (24 h). b Representative images of S100A4 immunofluorescence labeling in human PASMC after normoxia and hypoxia treatment. c Schematic representation of potential HRE in upstream and downstream sequence from S100A4 coding site. d EMSA analyses of potential HREs [HRE1:-4694, HRE2:857, HRE3:1359]. Slots were loaded as follows: 1: Labeled Probe only, 2: Labeled Probe and Nuclear extract (24 h normoxia), 3 Labeled Probe, Nuclear extract (24 h hypoxia), 4: Labeled Probe, Nuclear extract (24 h hypoxia) and Competitor. e Supershift analysis: 1: Labeled Probe only, 2: Labeled Probe and Nuclear extract (24 h hypoxia), 3 Labeled Probe, Nuclear extract (24 h hypoxia) and Competitor, 4: Labeled Probe, Nuclear extract (24 h hypoxia) and Antibody against HIF-1, 5: Labeled Probe, Nuclear extract (24 h hypoxia) and Antibody against HIF-2. Arrows represent specific band. f Real-time analysis of S100A4 expression after pretreatment of human PASMC with siRNA against HIF1, HIF2 or EGR1. ΔCt- relative expression of S100A4 to reference gene. siR- siRandom. g Immunofluorescence labeling of S100A4, SMC-actin and DAPI
