Figure 1.
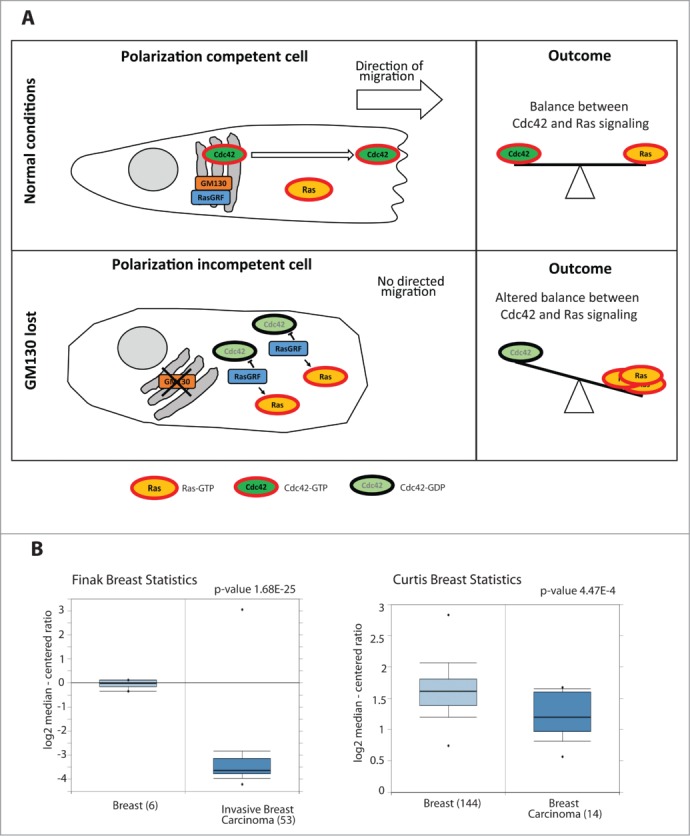
(A) Schematic representing the mechanism of action of GM130: GM130 binds to RasGRF and blocks its function. Once Cdc42 is activated, it accumulates on membranes and the Golgi sends Cdc42 in a polarized fashion to the Leading Edge of the migrating cell, thereby conferring persistence to the migration. GM130 will therefore contribute to maintain the balance between Cdc42 and Ras signaling. When GM130 is lost, the cell cannot migrate persistently and there is an imbalance between Cdc42 and Ras signaling. (B) Box Plots of two studies 32,33 comparing the mRNA levels of GM130 in normal tissues and in breast cancer tissues (obtained from Oncomine).
