Figure 1.
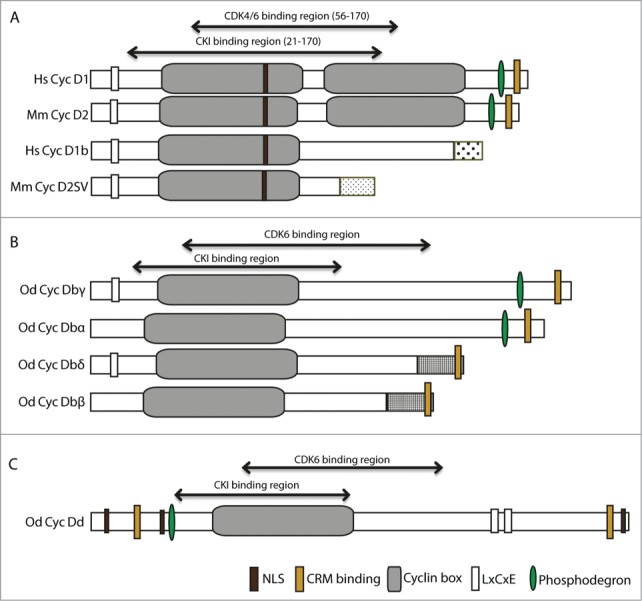
Functional domains in human and Oikopleura dioica Cyclin D splice variants. (A) Human Cyclin D1 and mouse Cyclin D2 and their splice variants, D1b and D2SV, respectively. (B) O. dioica Cyclin Db splice variants cover all presence/absence combinations (+/+, −/+, +/−, −/−) of the Retinoblastoma(Rb)-binding and phosphodegron domains, respectively. (C) O. dioica Cyclin Dd. NLS, Nuclear Localization Sequence; CRM, (Chromosomal maintenance 1 or Exportin 1) interaction motif; LxCxE Rb-binding motif. All motifs were predicted by SMART65 and ELM.66 Cyclin-dependent Kinase 6 (CDK6) and CDK inhibitor (CKI) binding regions on O. dioica Cyclin D splice variants were based on Zwicker et al.44 Unique C-terminal sequences arising in splice variants are indicated by different stippling patterns. BLAST and secondary structure assessments (PsiPred) of the C-termini of O. dioica Cyclin D variants show residual signatures of a second Cyclin box with low confidence scores.24 Hs, Human; Mm, Mouse; Od, O. dioica.
