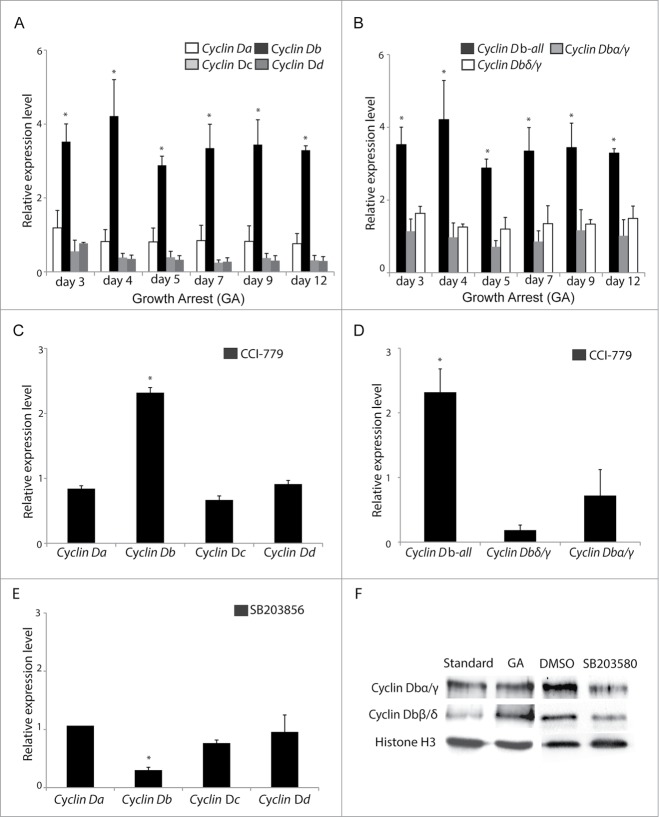
Figure 6.
(See previous page). Increased cyclin Dbβ levels during TOR inhibition require MAPK-p38 signaling. (A) Cyclin Db expression increased (*P < 0.05) and persisted at higher levels in O. dioica cultured under dense conditions where growth-arrest occurs. Under these same conditions, no significant change in expression of cyclin Da, cyclin Dc, cyclin Dd was observed. (B) The observed increase in cyclin Db expression during growth arrest was restricted to the β splice variant, as levels of the α, γ and δ splice variants were unaffected. (C) When animals were cultured under standard conditions but in the presence of the TOR inhibitor CCI-779 for 24 h, cyclin Db transcripts were upregulated (*P < 0.05) whereas cyclin Da, Dc, and Dd transcripts were not. (D) Similar to the results in (B) under growth arrest, at dense culture conditions, inhibition of TOR signaling under standard culture conditions resulted in upregulation of the Cyclin Dbβ splice variant (*P < 0.05), whereas levels of the α, γ and δ splice variants were unaffected. (E) When animals were cultured under standard conditions, but in the presence of the MAPK p38 inhibitor, SB203580, for 24 h at day 3, cyclin Db transcript levels were reduced (*P < 0.05), whereas cyclin Da, cyclin Dc, cyclin Dd transcript levels were not. Expression levels are relative to those observed in day 3 animals cultured under standard conditions (with addition of DMSO in controls when chemical inhibitors were used). Error bars indicate standard errors. (F) Western blots showed that Cyclin Dbα/γ levels were similar under standard culture or growth arrested (GA) conditions, whereas Cyclin Dbβ/δ levels increased under the latter conditions. Levels of all Cyclin Db splice variants decreased in the presence of MAPK p38 inhibitor SB203580.