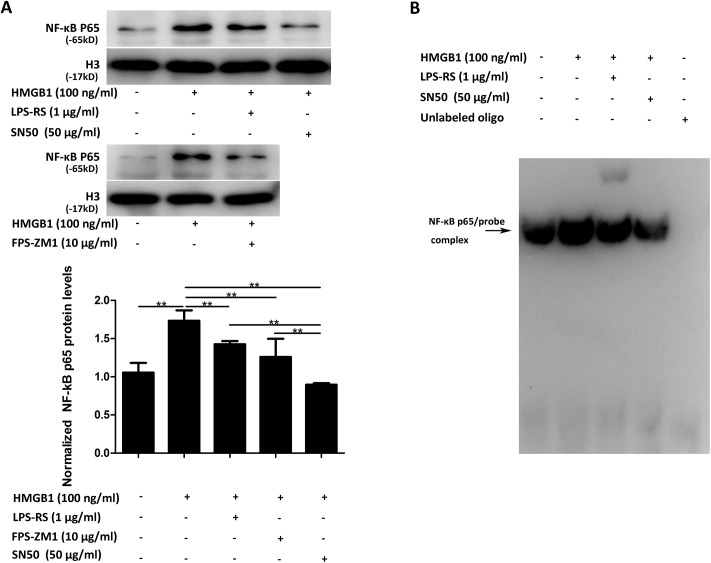
Fig 7. TLR4 and RAGE were involved in HMGB1-induced activation of NF-κB in bEnd.3 cells.
(A) Nuclear NF-κB p65 protein levels in bEnd.3 cells treated with HMGB1 plus different inhibitors. Inhibition of TLR4 and RAGE resulted in a significant decrease in HMGB1-induced NF-κB p65 translocation to nuclei. (B) NF-κB DNA-binding activity in bEnd.3 cells treated with HMGB1 plus different inhibitors detected by EMSA. HMGB1 increased NF-κB p65 binding activity to DNA in bEnd.3 cells while inhibition of TLR4 or SN50 attenuated this effect of HMGB1. Data were shown as mean±SD; n = 3. **P<0.01. HMGB1, high-mobility group box-1; EMSA, electrophoretic mobility shift assay; LPS-RS, lipopolysaccharide from Rhodobacter sphaeroides; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; SD, standard deviation; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end products.