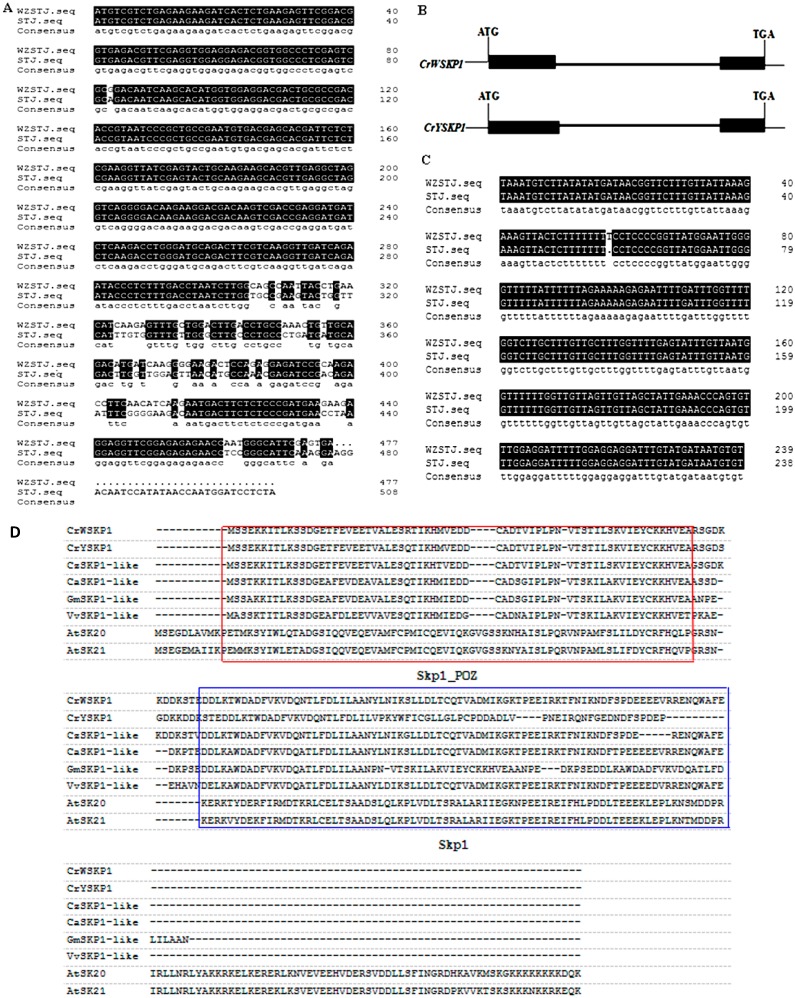
Figure 1.
Analyses of CrWSKP1 and CrYSKP1 genes. (A) Alignments of cDNA sequences of CrWSKP1 and CrYSKP1 genes between “Wuzishatangju” (WZSTJ) and “Shatangju” (STJ); (B) Exon-introns structure of CrWSKP1 and CrYSKP1 genes. CrWSKP1, DNA sequence of the Skp1-like gene from “Wuzishatangju”; CrYSKP1, DNA sequence of the Skp1-like gene from “Shatangju”. Solid boxes indicate exons, and bold lines represent introns; (C) Alignments of partial DNA sequences of CrWSKP1 and CrYSKP1 genes between “Wuzishatangju” (WZSTJ) and “Shatangju” (STJ); (D) Alignments of the putative amino acid sequences of CrWSKP1 and CrYSKP1 genes from different plant species. CrWSKP1 (“Wuzishatangju”), CrYSKP1 (“Shatangju”), CzSSKP1-like (Citrus maxima, ACP20181), CaSKP1-like (Cicer arietinum, XP004512164), GmSKP1-like (Glycine max, XP003517160), VvSKP1-like (Vitis vinifera, XP002279232), AtSK20 (Arabidopsis thaliana, A8MQG7), AtSK21 (Arabidopsis thaliana, Q8LF97). Higher conserved regions were marked in box with Skp1_POZ and Skp1.