Figure 6.
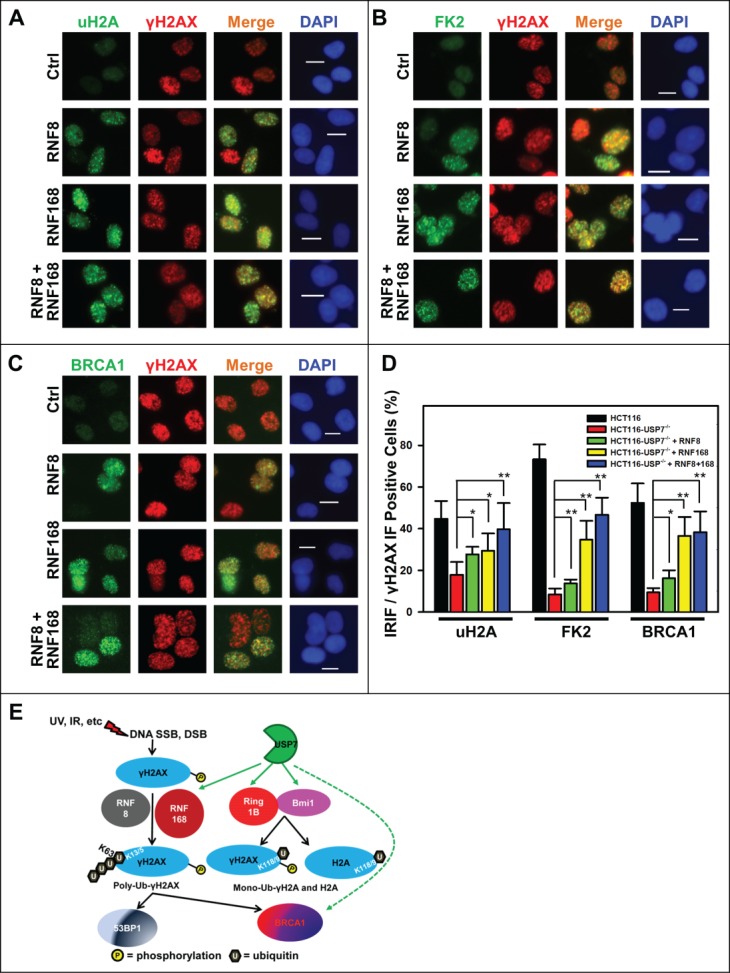
Adenovirus-mediated expression of RNF168 and RNF8 or168 partially rescues the formation of IRIF of uH2A, FK2 and BRCA1 in HCT116-USP7−/− cells. (A) HCT116-USP7−/− cells were infected with the indicated adenoviral vectors as in Figure 5. The infected cells were exposed to IR at 10 Gy. One hour after IR, sub-nuclear foci formations as IRIF of uH2A, γH2AX, FK2 and BRCA1 were visualized by immunofluorescence using specific antibodies. (A) IRIF of uH2A and γH2AX. (B) IRIF of FK2 and γH2AX. (C) IRIF of BRCA1 and γH2AX. (D) Bar graph illustrates quantitative data of IRIF of γH2AX, uH2A, FK2 and BRCA1. Mean ± SD of IRIF vs. γH2AX positive cell ratio was calculated from 4–6 microscopic fields of 3 independent experiments. Symbol * indicates P ≤ 0.05; Symbol ** indicates P ≤ 0.01. Calibration bar is 10 μm. (E) Graphic illustration of regulation of DDR by USP7. Upon DNA damage, phosphorylation of H2AX is triggered by DNA strand-breaks and accumulated at damage sites. γH2AX is subsequently ubiquitinated by the concerted action of RNF168 and RNF8. The ubiquitinated γH2AX in turn facilitates the accumulation of repair factor BRCA1 and 53BP1. USP7 (green hue) regulates polyubiquitination of γH2AX, mono-ubiquitination of γH2AX and H2A through modulating the stability of RNF168, Ring1B and Bmi1 E3 ligases (red hue). USP7 may also directly regulate stability of BRCA1.
