Figure 2.
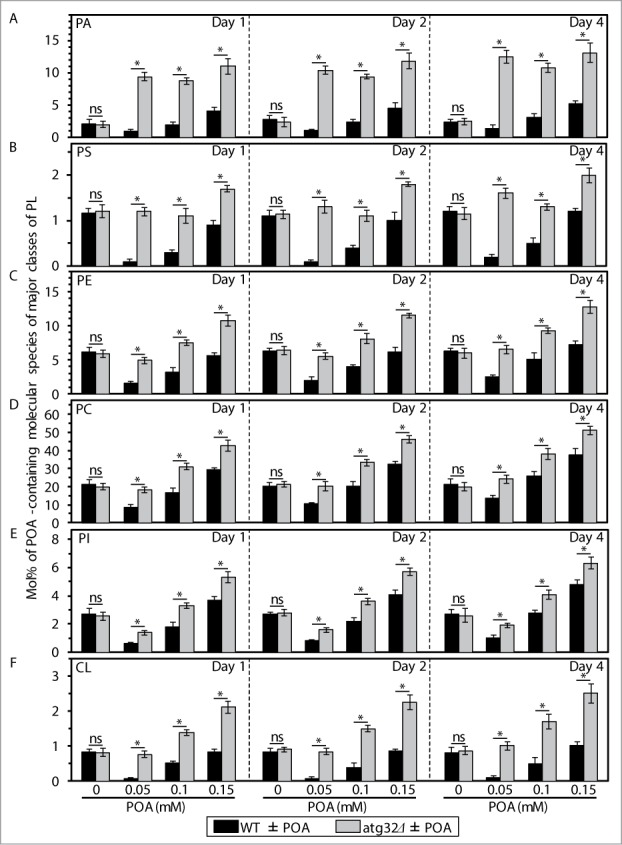
An exposure of WT cells to various concentrations of exogenous POA elicits differential effects on the relative levels of C16:1 molecular species (i.e., POA-containing species) of all major classes of PL, and the atg32Δ-dependent mutational block of mitophagy alters these effects. WT and atg32Δ cells were recovered at days 1, 2 and 4 of culturing in YP medium initially containing 0.2% glucose as carbon source. Extraction of cellular lipids, and mass spectrometric identification and quantitation of various molecular species of phospholipids (PL) were carried out as described in Materials and Methods. The relative level of POA-containing molecular species for each class of PL (i.e., PA, PS, PE, PC, PtdIns and CL) was calculated as mol% of all these PL classes. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 3; *P < 0.01; ns, not significant). For the PA, PS, PE, PC and PI classes of PL, POA-containing molecular species are the C32:1, C32:2, C34:1 and C34:2 species of each of them. For the CL class of PL, POA-containing molecular species are its C64:4, C66:4, C68:4, C70:4 species.
