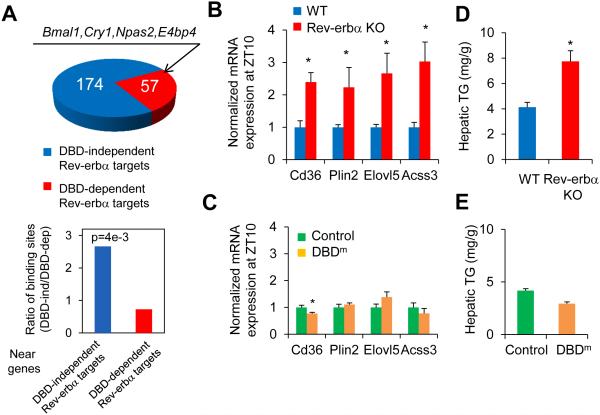
Figure 4. DBD-independent Rev-erbα sites regulate metabolic genes in liver.
(A) Top panel shows the number of DBD-dependent and -independent Rev-erbα target genes identified using microarrays in Rev-erbα KO (9) and DBDm mice (12). Bar graph shows ratios of DBD-independent and -dependent Rev-erbα/HDAC3 binding sites (29) located near two groups of Rev-erbα target genes (P value from hypergeometric test). (B) mRNA expression of lipid metabolic genes normalized to Arpp, measured by RT-qPCR, in livers of Rev-erba KO mice and wild type mice at ZT10. (C) mRNA expression of lipid metabolic genes normalized to Arpp, measured by RT-qPCR, in livers of Rev-erbα DBDm (Rev-erbα/β double floxed mice injected with AAV-Tbg-Cre) or control mice (floxed mice injected with AAV-Tbg-GFP) at ZT10. Data are expressed as mean± SEM (* Student’s t-test, p<0.05, n=4 per group). (D) Hepatic triglyceride (TG) levels in the same mice as in B. (E) Hepatic TG levels in mice as in C (* Student’s t-test, p<0.05, n=4 per group).