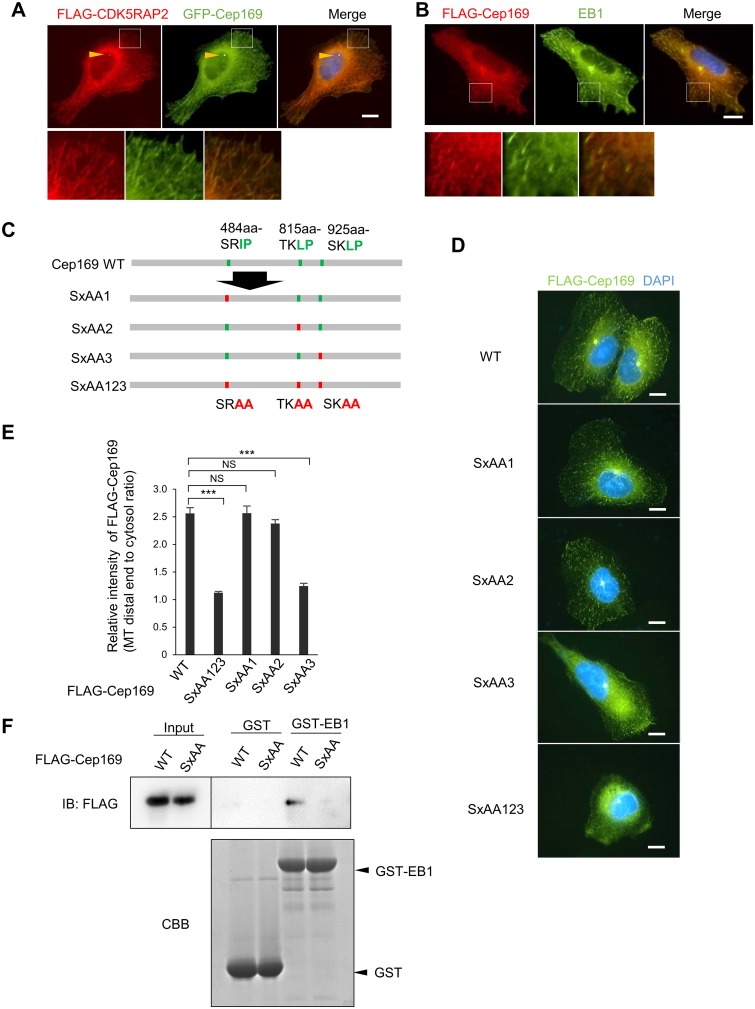
Fig 3. Cep169 targets MT distal ends in a manner dependent on the interaction with EB1.
(A) Immunofluorescence images showing co-localization of FLAG-tagged CDK5RAP2 and GFP-Cep169 at centrosome (arrowheads) and distal ends in U2OS cells probed with anti-FLAG antibody. (Scale bar, 10 μm). (B) Immunofluorescence images showing co-localization of FLAG-Cep169 and EB1 at distal ends in stable U2OS cell probed with anti-FLAG and EB1 antibodies. (Scale bar, 10 μm). (C) Schema of Cep169 showing the three (S/T)x(I/L)P motifs (up) and their alanine-substituted mutants (bottom). (D) Immunofluorescence image of Cep169 localization in U2OS cells transfected with FLAG-tagged wild type or alanine-substituted mutants of each (S/T)x(I/L)P motif in Cep169, as described in (C). (Scale bars, 10 μm). (E) Relative intensity of wild type or mutant Cep169 at distal ends. (n = 60 cells for each case; error bars, S.E.). P values result from t-test (***P < 0.0001, NS: not significant). (F) Pull-down assays using recombinant GST-EB1 as an affinity matrix to isolate FLAG-Cep169 WT or SxAA123 mutant. FLAG-Cep169 or GST and GST-EB1 proteins were analyzed with IB using anti-FLAG antibody or Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining, respectively.