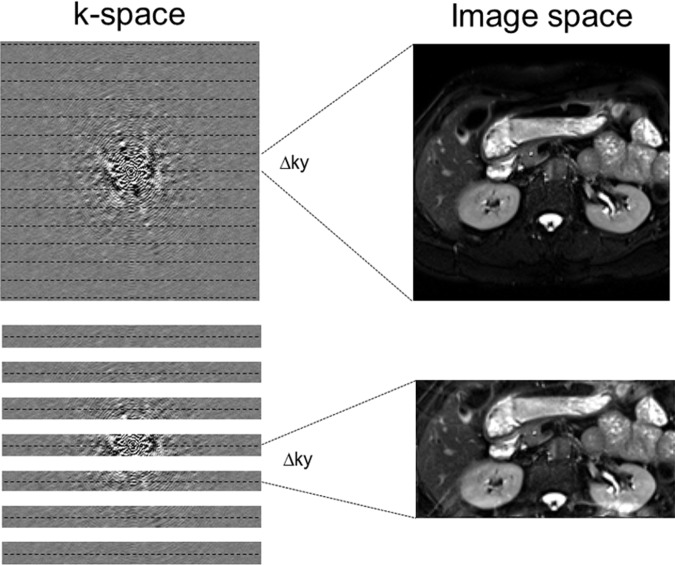
Figure 19.
Aliasing and undersampling of k-space. Top row: Aliasing, or wraparound artifact, occurs when the FOV of encoding is smaller than the imaged anatomic structures. The finer the sampling in k-space (eg, smaller Δky), the larger the FOV dimension of the image. Bottom row: When k-space is sampled only with every other line, the Δky is doubled and the FOV is halved, leading to aliasing caused by the undersampling. Parallel acquisition techniques such as GRAPPA or SENSE are used to synthesize the missing lines from the undersampling in k-space and therefore remove the aliasing.