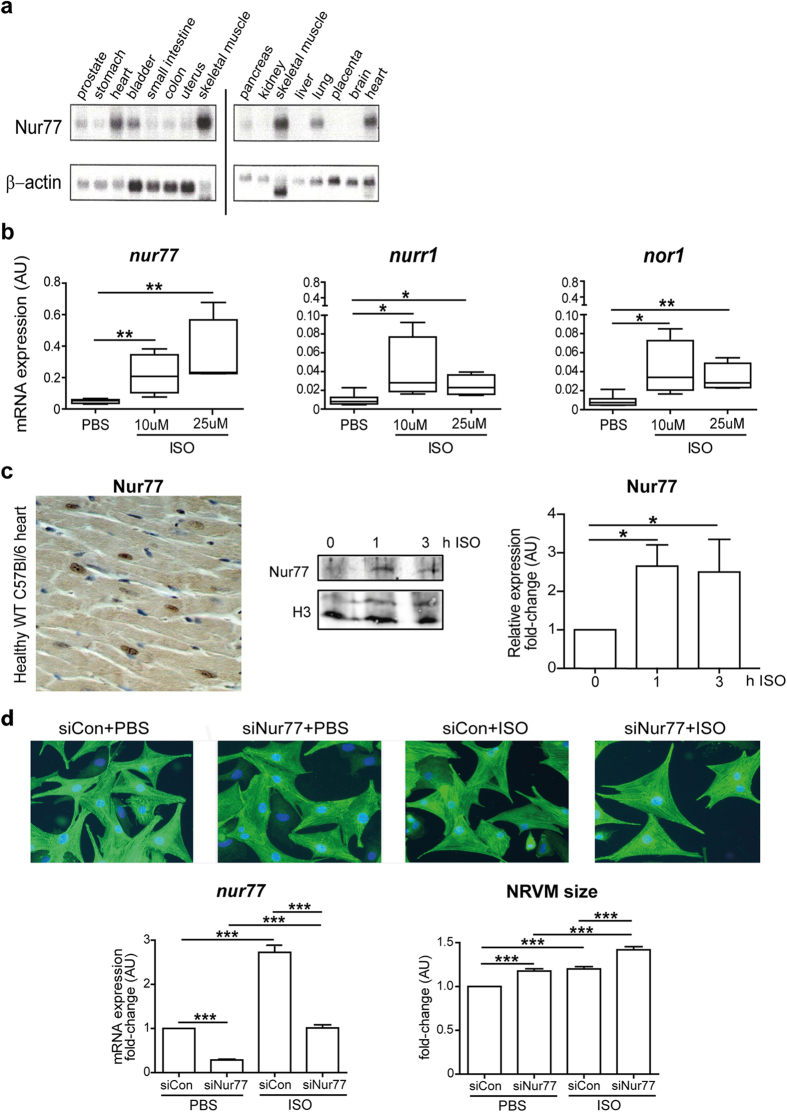
Figure 1. Isoproterenol increases Nur77 expression in cardiomyocytes and Nur77 knockdown enhances isoproterenol-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.
(a) Northern blot analysis of Nur77 expression in healthy human tissues. Heart and skeletal muscle exhibited highest endogenous Nur77 expression relative to loading control β-actin. Blots have been prepared under the same experimental conditions. (b) Significantly up-regulated NR4A gene expression in NRVMs after 1 h of isoproterenol (ISO) stimulation (n = 3), with Nur77 mRNA levels showing highest abundance. (c) Representative example of nuclear Nur77 protein expression in cardiomyocytes of healthy WT C57Bl/6 mice as assessed by immunohistochemistry. Photomicrograph shown at 200× magnification. Nur77 protein expression is significantly enhanced in nuclei of NRVMs after isoproterenol stimulation for 1 and 3 h (n = 4). (d) NRVMs are significantly larger after siRNA-mediated Nur77 knockdown (siNur77) compared to control-transfected (siCon) cells under both control conditions and 48 h of isoproterenol stimulation, as assessed by α-Actinin staining in >250 cells per group (n = 3). Photomicrographs are shown at 200× magnification. Boxplots represent median, inter-quartile range and minimum/maximum values; bars represent mean + SEM; *p < 0.05, **p<0.01, ***p < 0.001.