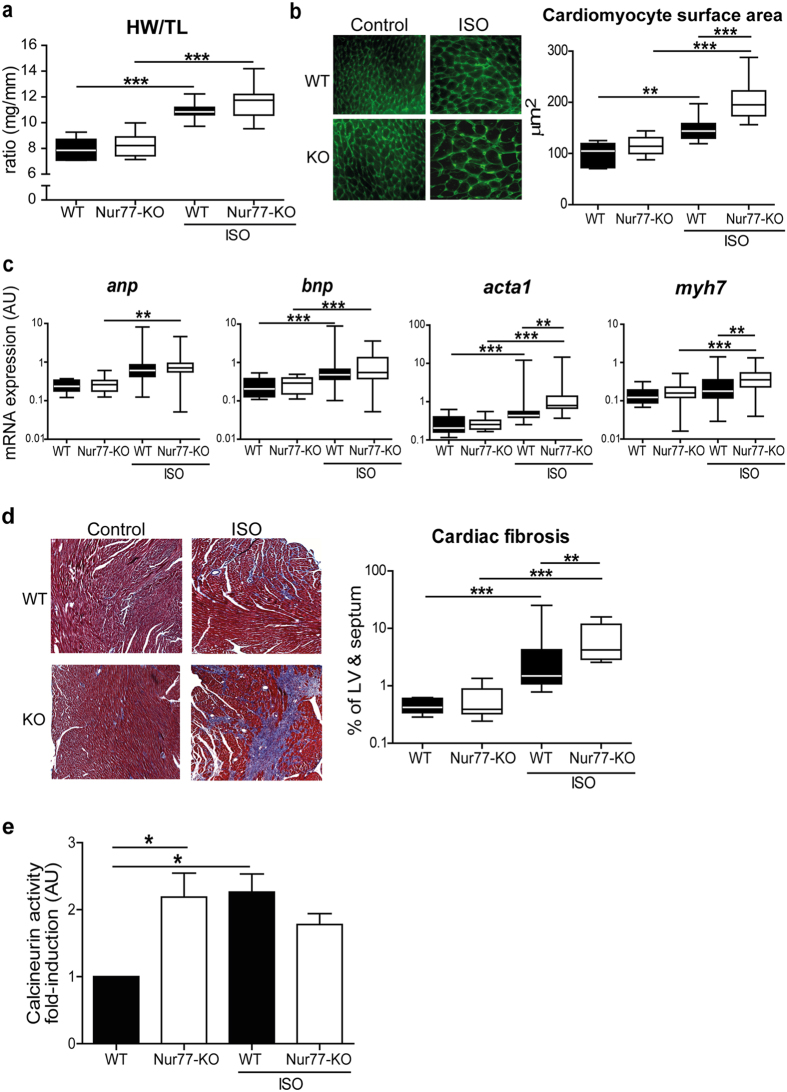
Figure 5. Nur77-KO mice exhibit enhanced adverse cardiac remodelling after chronic β-adrenergic stimulation.
WT (n = 16) and 13 surviving Nur77-KO mice were analysed after 1 week of chronic isoproterenol (ISO) infusion. (a) Heart weight/tibia length (HW/TL) ratio was higher after isoproterenol stimulation and further increased in Nur77-KO mice compared to WT mice. Tibia length did not differ between WT and Nur77-KO mice. (b) Cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area was significantly larger in isoproterenol-treated Nur77-KO mice compared to treated WT mice, as assessed by fluorescent wheat germ agglutinin staining in >75 cells per heart. Photomicrographs are shown at 630× magnification. (c) RT-PCR analysis showed significant up-regulation of foetal gene expression after isoproterenol treatment. Nur77-KO mice exhibited a significant increase in acta1 and myh7 after isoproterenol, when compared to WT. anp: atrial natriuretic peptide; bnp: brain natriuretic peptide; acta1: α1 skeletal actin; myh7: β-myosin heavy chain. (d) Collagen deposition was assessed by Masson’s Trichrome staining assessed by quantitative morphometry, photomicrographs are shown at 50× magnification. The left ventricle and septum of Nur77-KO mice was affected stronger by interstitial fibrosis (blue) after isoproterenol than WT mice. (e) Calcineurin phosphatase activity is significantly higher in myocardium of control Nur77-KO mice. After chronic isoproterenol stimulation, calcineurin activity is significantly enhanced in WT hearts, while it does not further increase in Nur77-KO mice compared to Nur77-KO control mice (n = 3–4 in each group). Boxplots represent median, inter-quartile range and minimum/maximum values; bars represent mean+SEM; *p < 0.05, **p <0.01, ***p < 0.001.