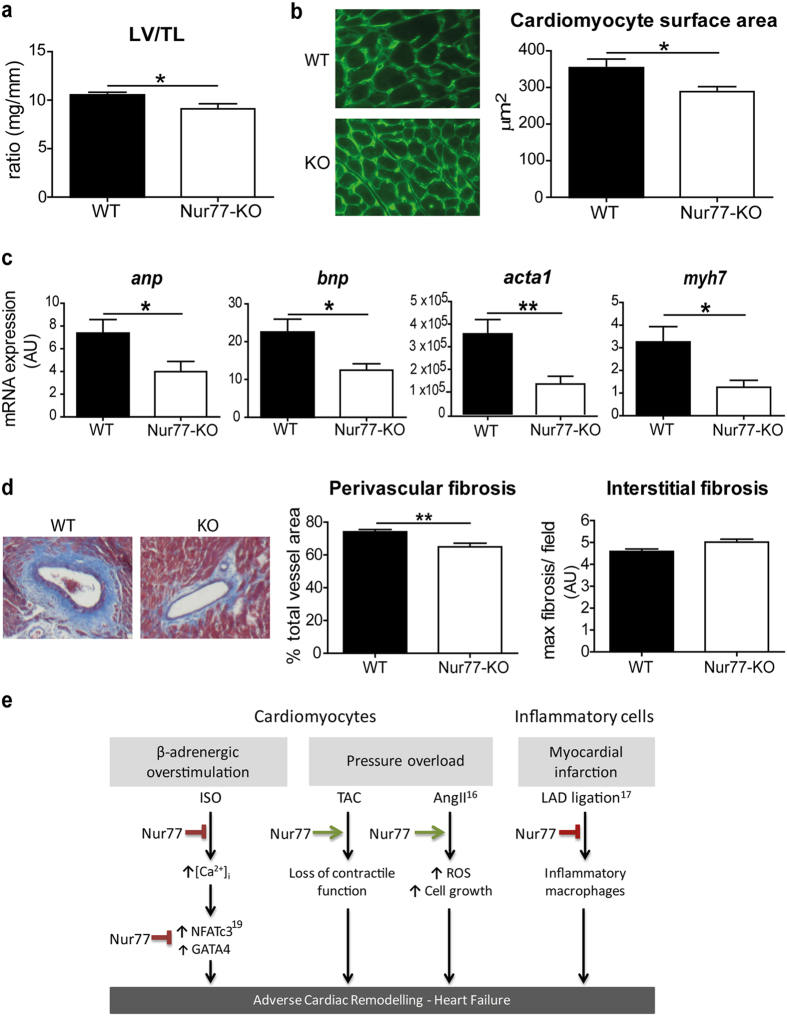
Figure 6. Attenuated pressure overload-induced adverse cardiac remodelling in Nur77-KO mice.
WT (n = 12) and Nur77-KO (n = 11) mice were analysed after 28 days of TAC. (a) Left ventricle/tibia length (LV/TL) ratio was significantly lower in Nur77-KO mice after TAC than in WT mice. Tibia length did not differ between WT and Nur77-KO mice. (b) Cardiomyocytes from Nur77-KO mice were significantly smaller compared to cardiomyocytes from WT mice, as assessed by fluorescent wheat germ agglutinin staining in >75 cells per heart. Photomicrographs are shown at 630× magnification. (c) Foetal gene expression after TAC was significantly down-regulated in Nur77-KO mice, as assessed by RT-PCR. anp: atrial natriuretic peptide; bnp: brain natriuretic peptide; acta1: α1 skeletal actin; myh7: β-myosin heavy chain. (d) Collagen deposition as assessed by Masson’s Trichrome staining, photomicrograph shown at 100× magnification. Significantly less perivascular fibrosis was present in Nur77-KO mice compared to WT, while areas of interstitial fibrosis were not different. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (e) Proposed mechanism for the role of Nur77 in cardiac remodelling induced by different insults. ISO: isoproterenol; TAC: transverse aortic constriction; AngII: angiotensin II; LAD: left anterior descending coronary artery; ROS: reactive oxygen species.