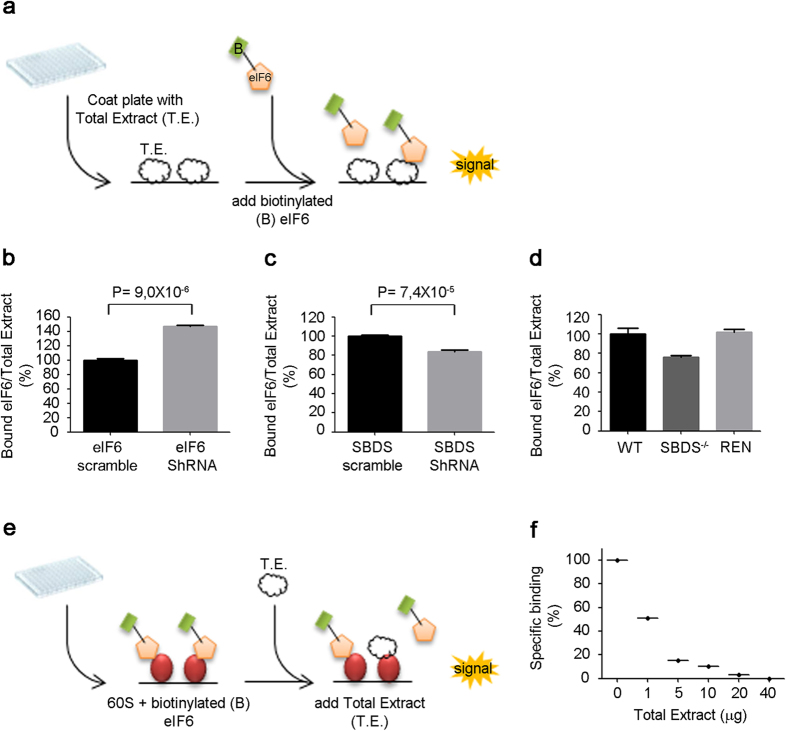
Figure 3. Measuring ribosomal binding sites on total extracts.
SBDS depletion reduces eIF6 binding sites. (a) Experimental design with immobilized extracts and labeled eIF6. (b) In vivo eIF6 sh-RNA increases in vitro available 60S sites. Equal amounts of extracts from either control cells (scramble, black) or eIF6-depleted cells (eIF6 ShRNA, grey) were incubated with labeled eIF6. (c) In vivo SBDS depletion decreases in vitro available 60S sites. Experimental design as in b). (d) SBDS-deficient fibroblasts have less binding sites for eIF6, respect to wt and REN cell line24. In this case we used a cell line with genetically inactivated SBDS (SBDS −/−) and we compared it to a matched wt or to a mesothelioma cell line (e) Design of activity evaluation for eIF6 release. (f) eIF6 is released by cellular extracts. After having performed total eIF6 binding on immobilized ribosomes, given amounts of extracts were added, and residual eIF6 binding was measured. All the experiments were performed at least five times. Mean + SD. T-Test, paired, two-tailed.